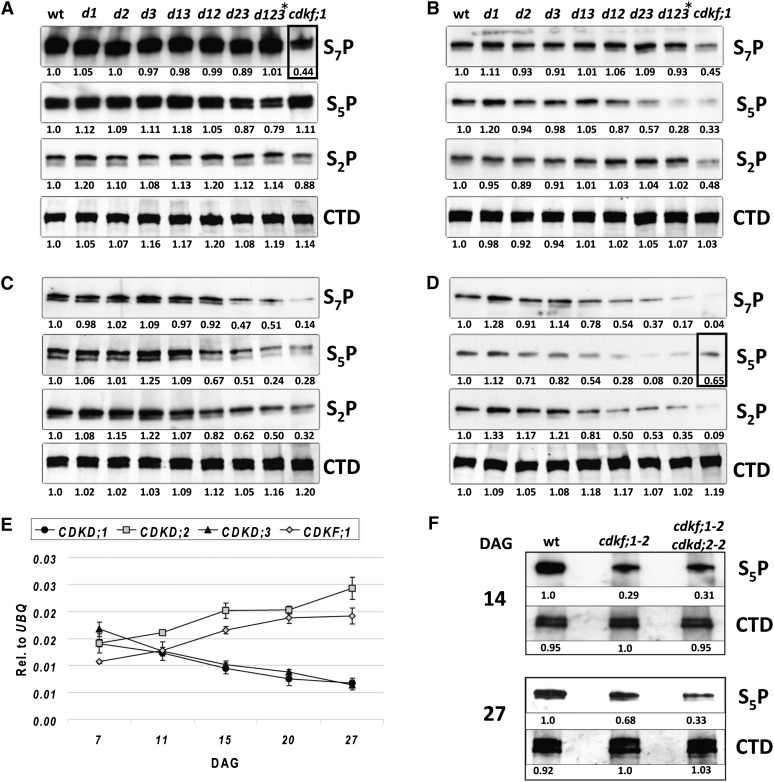
Figure 4.
Developmental Alterations of Position-Specific Ser Phosphorylation of RNAPII CTD in the cdkf;1 and cdkd Single, Double, and Triple Mutants during Seedling Development.
(A) to (D) Quantitative analysis of position-specific CTD Ser phosphorylation with CTD S2P-, S5P-, and S7P-specific antibodies at 7 (A), 14 (B), 20 (C), and 27 (D) DAG. Equal loading of protein samples is indicated by immunoblotting with anti-CTD antibody 4H8 (CTD). Quantitative changes indicated by numerical values were normalized to wild-type control in each lane. Allelic combinations of different cdkd mutants is the same as in Figure 2H, except for d123*, which is cdkd;1-1 cdkd;2-1 (cdkd;3-1/cdkd;3-2). Early reduction of S7P mark in cdkf;1-1 at 7 DAG and compensatory increase of S5P level in cdkf;1-1 at 27 DAG are indicated by frames. wt, wild type.
(E) qRT-PCR comparison of CDKF;1 and CDKD transcript levels relative to UBQ5 standard at different stages of seedling development. The error bars represent sd of the mean of triplicate qRT-PCR measurements using three biological replicates.
(F) Immunoblot analysis with S5P-specific monoclonal antibody indicates that, compared with 14-d-old mutants, enhanced CDKD;2 expression confers a compensatory increase of CTD S5P mark at 27 DAG in cdkf;1-2 seedlings, which is not detectable in the cdkf;1-2 cdkd;2-2 double mutant.