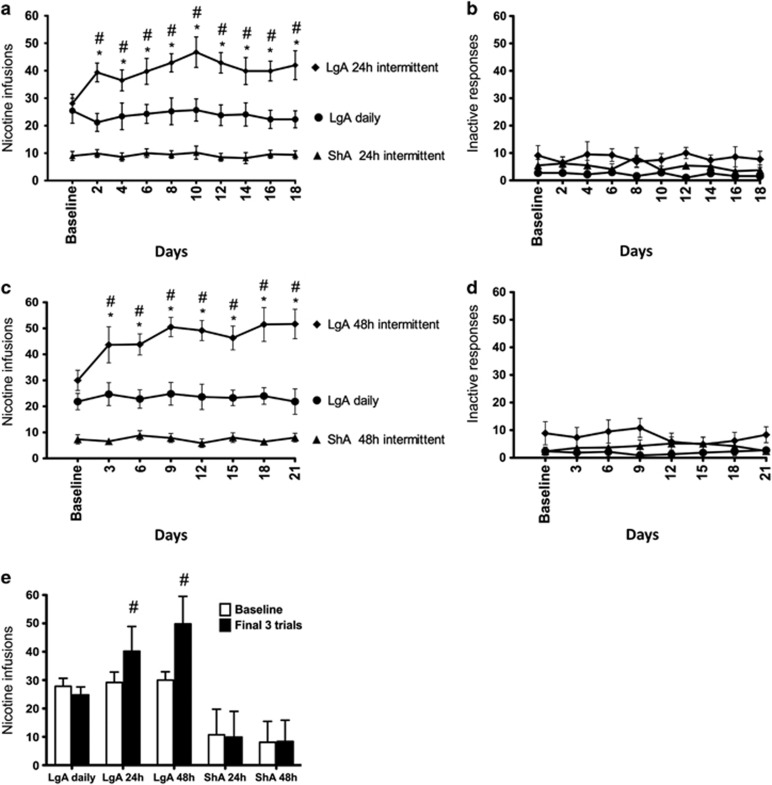
Figure 2.
Nicotine intake (mean±SEM) in rats that self-administered nicotine under a fixed-ratio (FR)1 schedule in either 21 h (long access (LgA)) or 1 h (short access (ShA)) sessions. LgA rats increased their nicotine intake on an intermittent schedule with 24–48 h breaks between sessions, whereas LgA rats on a daily schedule did not. (a) Total number of nicotine infusions per session when the intermittent schedule included 24 h breaks between sessions. (b) Total number of inactive operant responses per session when the intermittent schedule included 24 h breaks between sessions. (c) Total number of nicotine infusions per session when the intermittent schedule included 48 h breaks between sessions. (d) Total number of inactive operant responses per session when the intermittent schedule included 48 h breaks between sessions. (e) Total number of nicotine infusions during baseline (ie, last 3 days of self-administration before separating the rats into daily and intermittent conditions; see Figure 1) vs the last 3 days of daily/intermittent nicotine self-administration. #p<0.05, compared with baseline; *p<0.05, compared with daily self-administration group. n=8–10 per group.