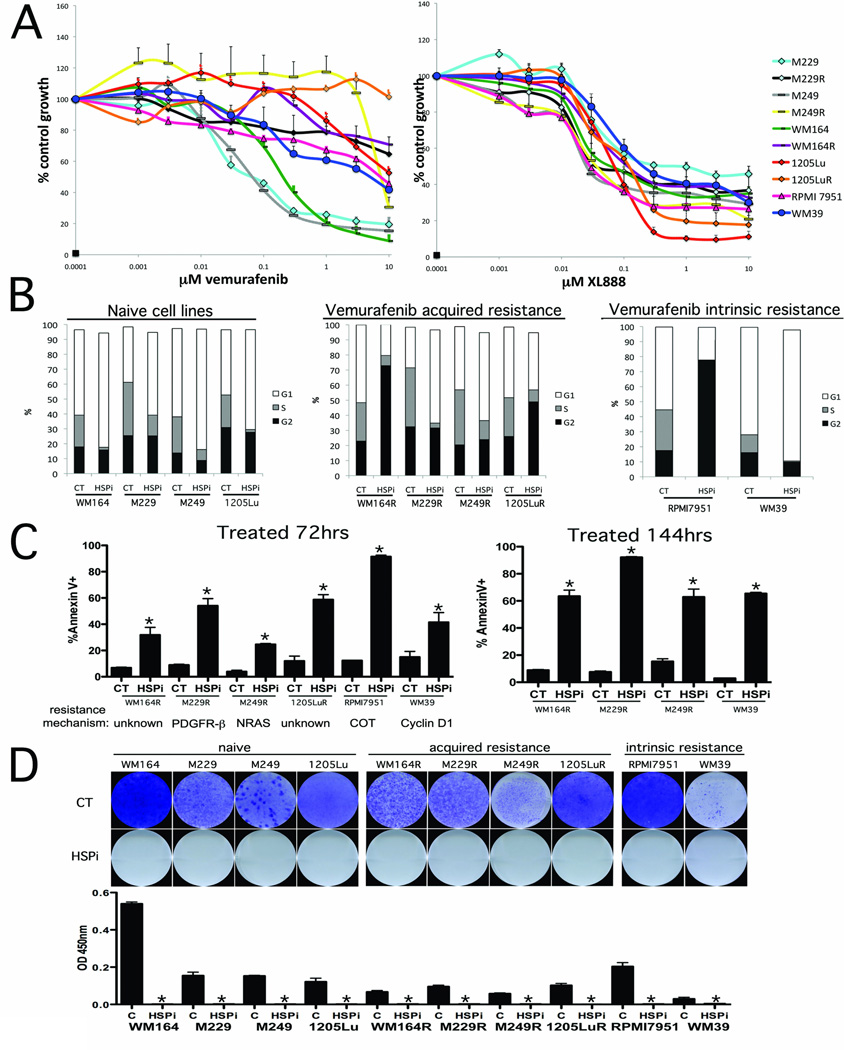
Figure 1. The HSP90 inhibitor XL888 blocks the growth and survival of melanoma cell lines with diverse mechanisms of vemurafenib resistance.
A: Growth assay showing the response of matched pairs of vemurafenib naïve and resistant melanoma cell lines and melanoma cell lines with intrinsic resistance. (Left) Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of vemurafenib (1nM – 10 µM: 72 hrs) before being subject to the MTT assay. (Right) Cell growth assay showing the response of the cell line panel from (A) to the HSP90 inhibitor (1nM-10 µM: 72 hrs). B: Cell cycle effects of XL888 (300 nM: 24 hrs) upon vemurafenib sensitive and naïve cell lines. Cells were fixed, stained with propidium iodide and distributions analyzed by flow cytometry. C: XL888 induces apoptosis in every model of acquired vemurafenib resistance tested. Cells were treated for either 72 or 144 hrs with XL888 (300 nM) followed by Annexin-V. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. D: (Upper) Colony formation assay showing the long-term effectiveness of XL888. Cell lines were treated with 300nM XL888 for 4 weeks before being fixed and stained with crystal violet. (Lower) Quantification of absorbance after 4 weeks of drug treatment.