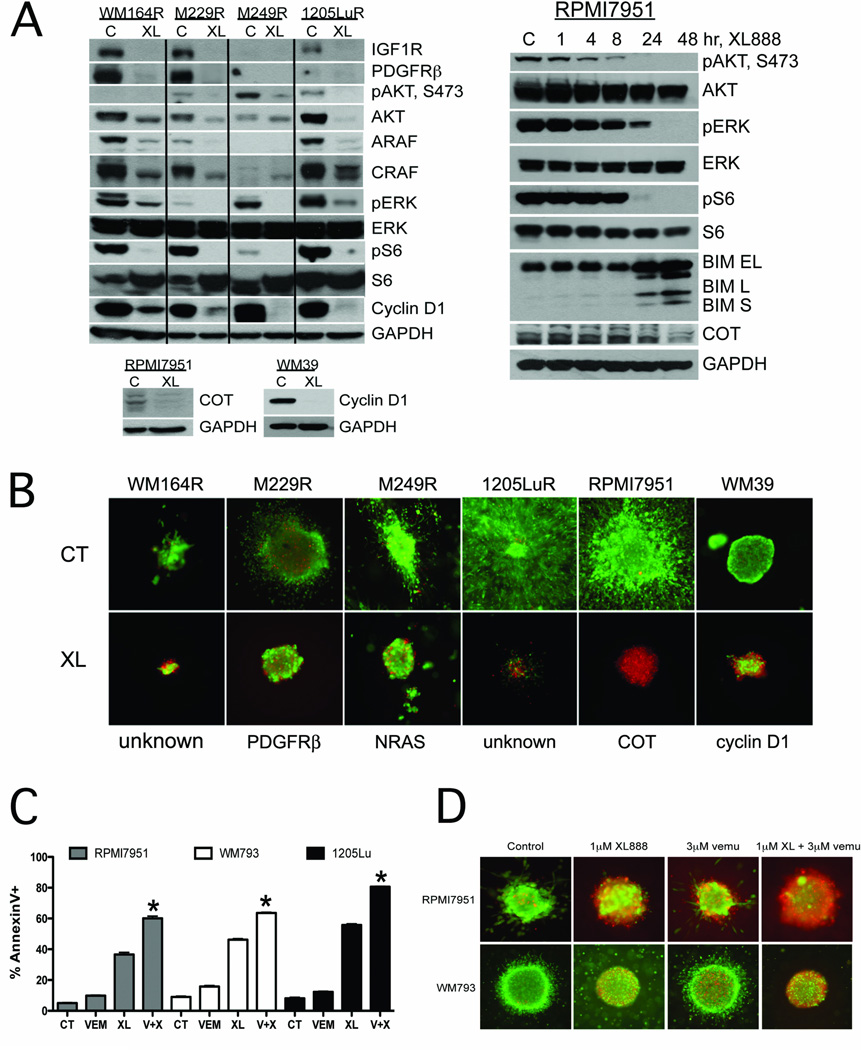
Figure 2. XL888 degrades proteins involved in BRAF inhibitor resistance leading to apoptosis induction.
A: (Left) XL888 degrades IGF1R, PDGFRβ, ARAF, CRAF and cyclin D1 and inhibits pAKT, pERK and pS6 signaling in 4 melanoma cell lines with acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance. XL888 degrades the expression of COT and cyclin D1 in melanoma cell lines with intrinsic resistance to vemurafenib. (Right) Time-dependency of the XL888 mediated effects upon pAKT, pERK, pS6, COT and BIM. RPMI7951 cells were treated with XL888 for 0–48 hrs. B: XL888 (1 µM, 144 hrs) is effective at blocking the growth and survival of vemurafenib resistant melanoma cell lines grown as 3D collagen implanted spheroids. Staining shows cell viability, where green corresponds to live cells and red: dead cells. Magnification X4. C: Combining XL888 with vemurafenib leads to enhanced levels of apoptosis in melanoma cell lines with COT overexpression (RPMI7951), or loss of PTEN expression (WM793 and 1205Lu). Cells were treated with vemurafenib (3 µM), XL888 (300nM), or the two in combination for 48 hr. Apoptosis was measured by Annexin-V staining and flow cytometry. D: XL888 in combination with vemurafenib reduces the survival of intrinsically resistant melanoma cell lines grown as 3D collagen-implanted spheroids. RPMI7951 cells (COT amplified) and WM793 cells (PTEN deficient) were treated with either XL888 (1 µM), vemurafenib (3 µM), or a combination of the two for 48 hrs. Viability was measured as described above.