Figure 8.
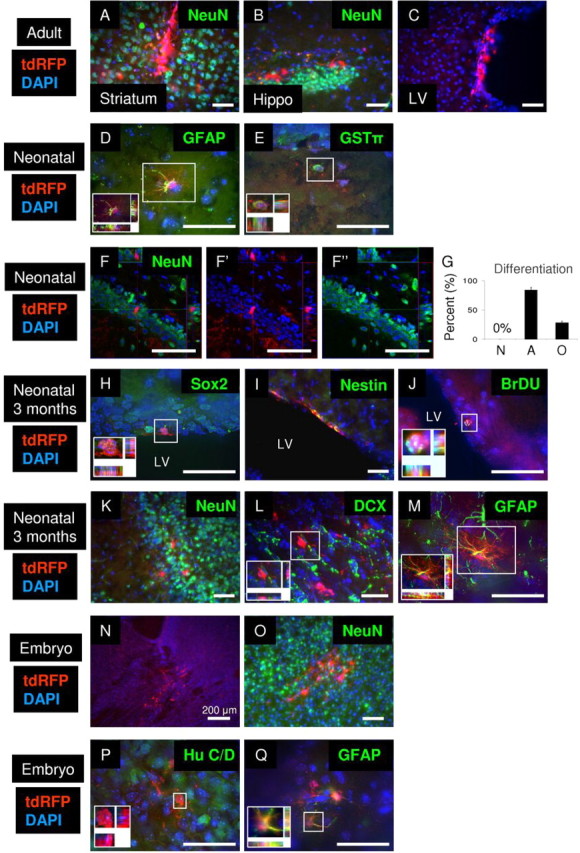
Rad-NSCs differentiate into astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in vivo after transplantation, but not neurons. A–C, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (tdRFP, red) did not differentiate into NeuN-positive neurons in the striatum (A, NeuN, green) or hippocampus (B, NeuN, green) in adult brains. C, Transplanted Rad-NSCs were observed in the lateral ventricle (LV) in adult brains, but did not migrate in the RMS. D, E, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (tdRFP, red) differentiated into GFAP-positive astrocytes (D, green) and GSTπ-positive oligodendrocytes (E, green) in the both white and gray matter of neonatal mice after transplantation. F, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (red) did not express NeuN (green) in the hippocampus. F′, F″, FITC and TRITC channels, respectively. G, Quantification of Rad-NSC differentiation 1 month after neonatal transplantation into whole brain. H, I, Three months after transplantation, tdRFP-positive Rad-NSCs (red) expressed Sox2 (H, green) or Nestin (I, green) in the SVZ. J, Three months after transplantation, tdRFP-positive Rad-NSCs (red) stained for BrdU (green) in the SVZ. K, L, tdRFP-positive Rad-NSCs (red) that migrated by the RMS did not express NeuN (K, green) or DCX (L, green) in the olfactory bulb 3 months after transplantation. M, tdRFP-positive Rad-NSCs (red) differentiated into GFAP-positive astrocytes (green) in the olfactory bulb 3 months after transplantation. N, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (red) were observed to engraft in E20 brains. O, P, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (tdRFP, red) did not differentiate into NeuN-positive (O, green) or Hu C/D-positive (P, green) neurons in E20 brains. Q, Transplanted Rad-NSCs (red) expressed GFAP protein in E20 brains. Cell nuclei are shown by DAPI staining (blue). Insets, Magnified deconvolution views of the white boxes. Scale bars: 50 μm.
