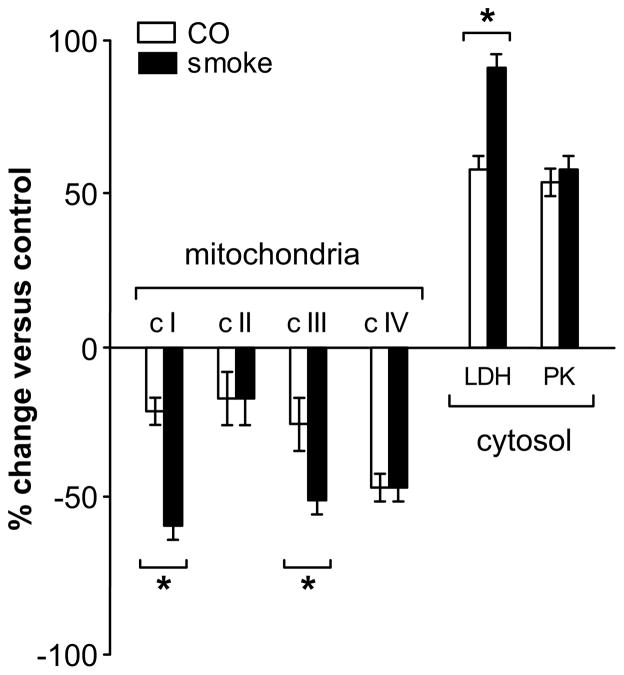
Figure 4.
Comparison of the magnitude of change in the individual respiratory activities at the 2-h recovery point after exposure to combustion smoke versus exposure to carbon monoxide. Inhibition of complexes I and III by smoke was greater than by CO, while inhibition of complex IV was identical with both exposures. * Indicates that at the 2-h recovery point, the change induced by exposure to smoke is different than the change induced by exposure to CO; P<0.05.