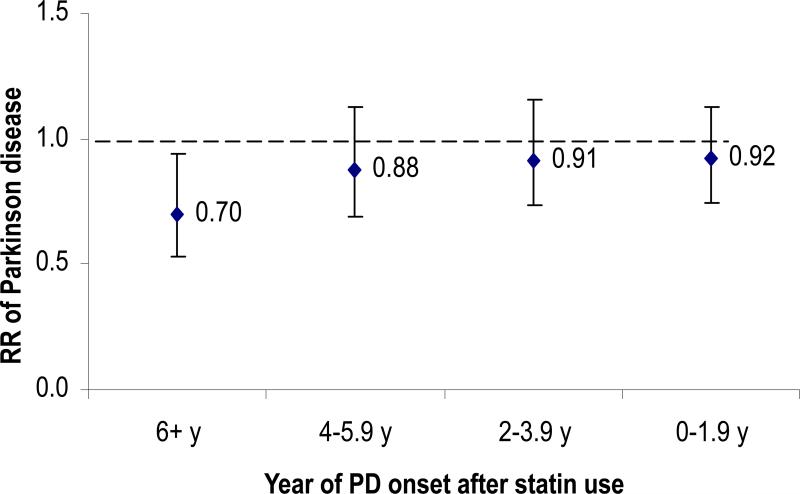
Figure 1.
Lag analysis of updated statin use and risk of developing PD, adjusted for age (in months), smoking status (never smoker, past smoker, current smoker with 1-14 cigarettes/d, or current smoker with ≥ 15 cigarettes/d), BMI (<23, 23-24.9, 25-26.9, 27-29.9, or ≥30 kg/m2), intake of caffeine (quintiles), lactose (quintiles), and alcohol (none, 1-4.9, 5-9.9, 10-14.9, or ≥15 g/d for women; none, 1-9.9, 10-19.9, 20-29.9, or ≥30 g/d for men), physical activity (quintiles), use of ibuprofen (yes/no), duration of hypercholesterolemia (years) and presence of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes (yes/no for each) .