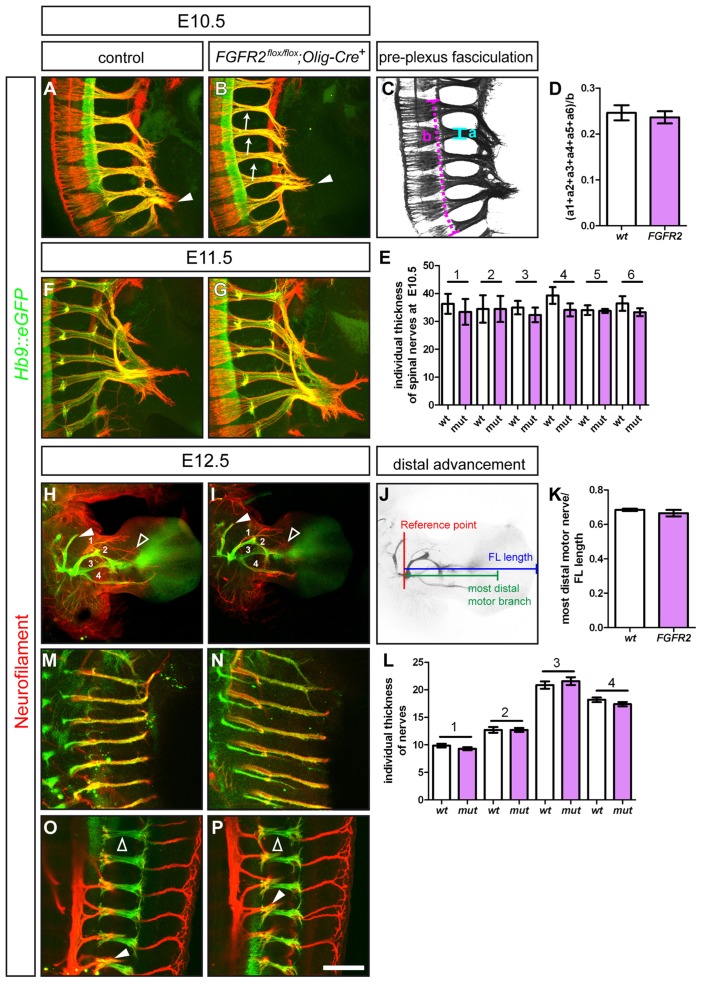
Figure 3. Ablation of FGFR2 from motor neurons does not impair fasciculation, extension and gross morphology of nerve projections.
Immunohistochemical staining of wholemount embryo preparations against Hb9::eGFP (green, motor nerves) and Neurofilament (red, motor and sensory nerves). At E10.5, tightly fasciculated spinal nerves have formed the brachial plexus at the base of the limb of control embryos (A) and in FGFR2flox/flox;Olig2-Cre+ mutant embryos (B). (C, D) Quantification of the pre-plexus fasciculation of the 6 spinal nerves that form the brachial plexus shows no differences between control (0.25±0.017 SEM) and FGFR2flox/flox;Olig2-Cre+ mutant embryos (0.24±0.013, p = 0,65). (E) Quantification of the individual thickness of spinal nerve branches that contribute fibers to the brachial plexus showed no significant difference between control and mutant embryos (p1 = 0,63, p2 = 0,99, p3 = 0,47, p4 = 0,20, p5 = 0,89, p6 = 0,32). (F, G) At E11.5, both in control and mutant embryos, first target specific fascicles have entered the limb mesenchyme. (H) Motor and sensory innervation of control embryo forelimbs. 1 = branch of the radial nerve, 2 = radial nerve, 3 = median nerve, 4 = ulnar nerve. (I) Gross morphology of motor and sensory innervation to the forelimb is not altered in embryos where FGFR2 was ablated in motor neurons by Olig2-Cre. (J, K) The distal advancement of the median nerve is not impaired in FGFR2flox/flox;Olig2-Cre+ mutant embryos (0.67±0.02) when compared to control littermates (0.68±0.01, p = 0,36). (L) Quantification of the individual thickness of the 4 major motor nerves shows not significant differences between control and mutant embryos in fasciculation (p1 = 0,24, p2 = 0,99, p3 = 0,47, p4 = 0,19). Innervation of intercostal muscles at thoracic levels forms tightly fasciculated nerve branches in control (M) and FGFR2flox/flox;Olig2-Cre+ mutant embryos (N). Also innervation of epaxial musculature by the ascending branch (empty arrowheads) of MMC projections is established normally in FGFR2flox/flox;Olig2-Cre+ mutant embryos (P) when compared to control embryos (O, arrowhead points to descending branch which innervates intercostal musculature). Scale bar in (P) equals 100 µm for A, B, F and G, 500 µm for H and I, and 200 µm for M and N, and 100 µm for O and P.