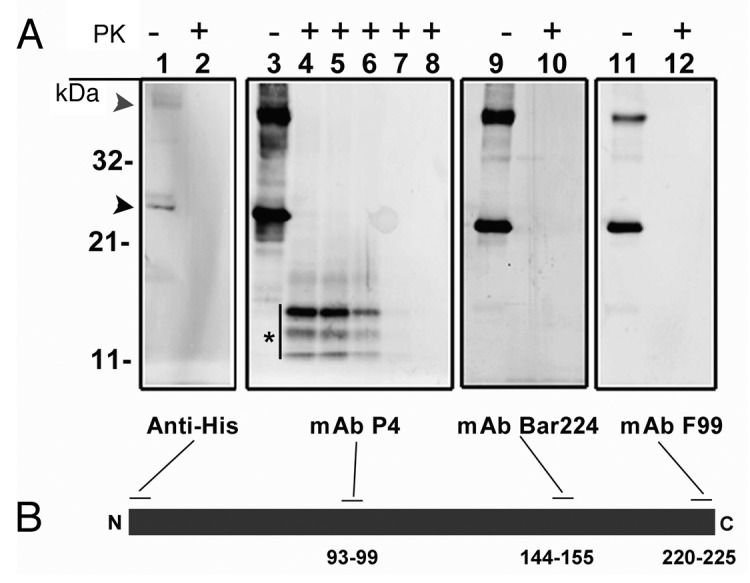
Figure 1. (A) western blot analysis of recombinant ovine PrP (rPrP), derived from bacterial inclusion bodies, with regard to proteinase sensitivity. A panel of four mAbs was used to map the N- and C-terminal ends (Anti-His and F99 respectively), the central (P4) and globular (BAR 224) domains. As shown in lanes 1, 3, 9 and 11, which were not treated with proteinase K, rPrP was detected by all mAbs with prominent dimeric (gray arrowhead) and monomeric (black arrowhead) forms. In lanes 2, 4, 10 and 12, samples were treated with proteinase K (5 µg/ml) at 22°C for 30 sec, which resulted in complete loss of signal from all mAbs except P4 which revealed a distinct triplet of bands (*), in the range of 11–14 kDa. In lanes 5, 6, 7 and 8 Proteinase K digestion continued for 1, 2, 5 and 10 min respectively. A rapid decline of signal was evident with no signal left after 10 min of Proteinase K treatment. (B) Schematic representation of rPrP with binding-sites for mAbs. Numbers refer to mAb epitopes in ovine PrP.
