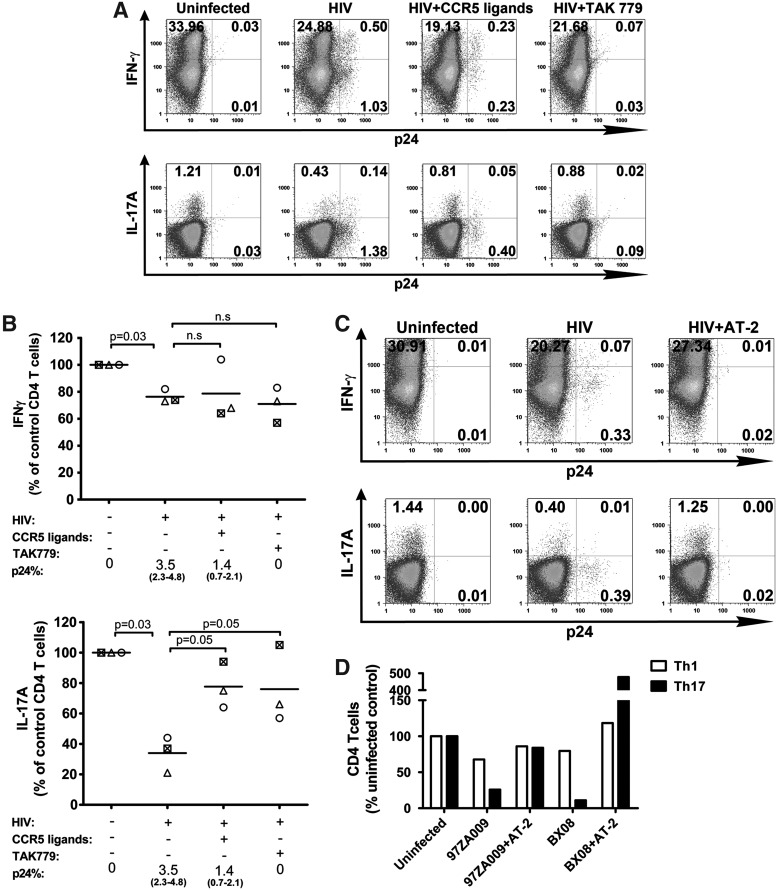
FIG. 2.
Th1 and Th17 responses in HIV-infected cultures treated with CCR5 ligands or TAK779. CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 48 h and then infected with HIV-1 97ZA009 in the presence of CCR5 ligands: MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and RANTES for 5 days. The RANTES antagonist TAK779 was also tested for comparison. Cells incubated with AT-2-inactivated HIV serve as controls. Cells were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 6 h, and stained with antibodies to p24, IFN-γ, and IL-17A. (A) Representative dot plots of CD4 T cells in uninfected cultures or infected cultures that were left untreated or treated with CCR5 ligands or TAK779. The percentages of CD4 T cells positive for IFN-γ, IL-17A, and p24 are shown. (B) Effects of CCR5 ligands or TAK779 on the frequencies of IFN-γ+ or IL-17A+ CD4 T cells in HIV-infected cultures. Data from each of the three different donors tested are depicted with different symbols. Frequencies of the respective CD4 T cells in the uninfected cultures from the same donors are normalized to 100%. p24% indicates the average and range of the percentages of CD4 T cells expressing p24 under the designated experimental conditions. Statistical significance was determined with the exact Wilcoxon rank sum test. (C) Representative dot plots from uninfected, HIV-infected, and AT-2-inactivated HIV-treated cultures showing the percentages of CD4 T cells expressing p24 and IFN-γ or IL-17A. (D) Relative percentages of CD4 T cells producing IFN-γ (Th1) and IL-17A (Th17) after exposure with infectious or inactivated HIV. Two R5-tropic HIV-1 isolates (97ZA009 and BX08) were tested. Frequencies of Th1 and Th17 cells in uninfected cultures are normalized to 100%.