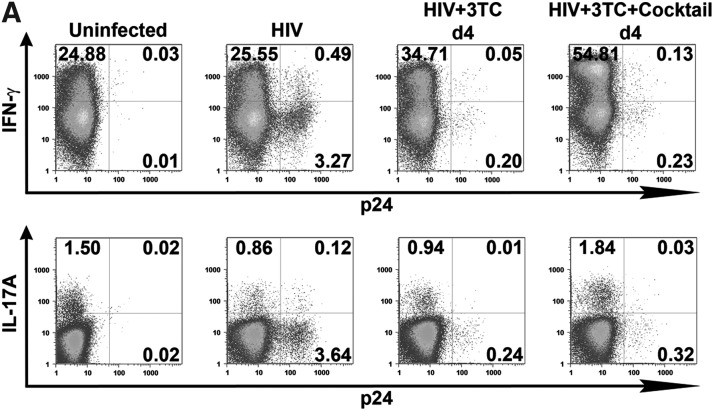
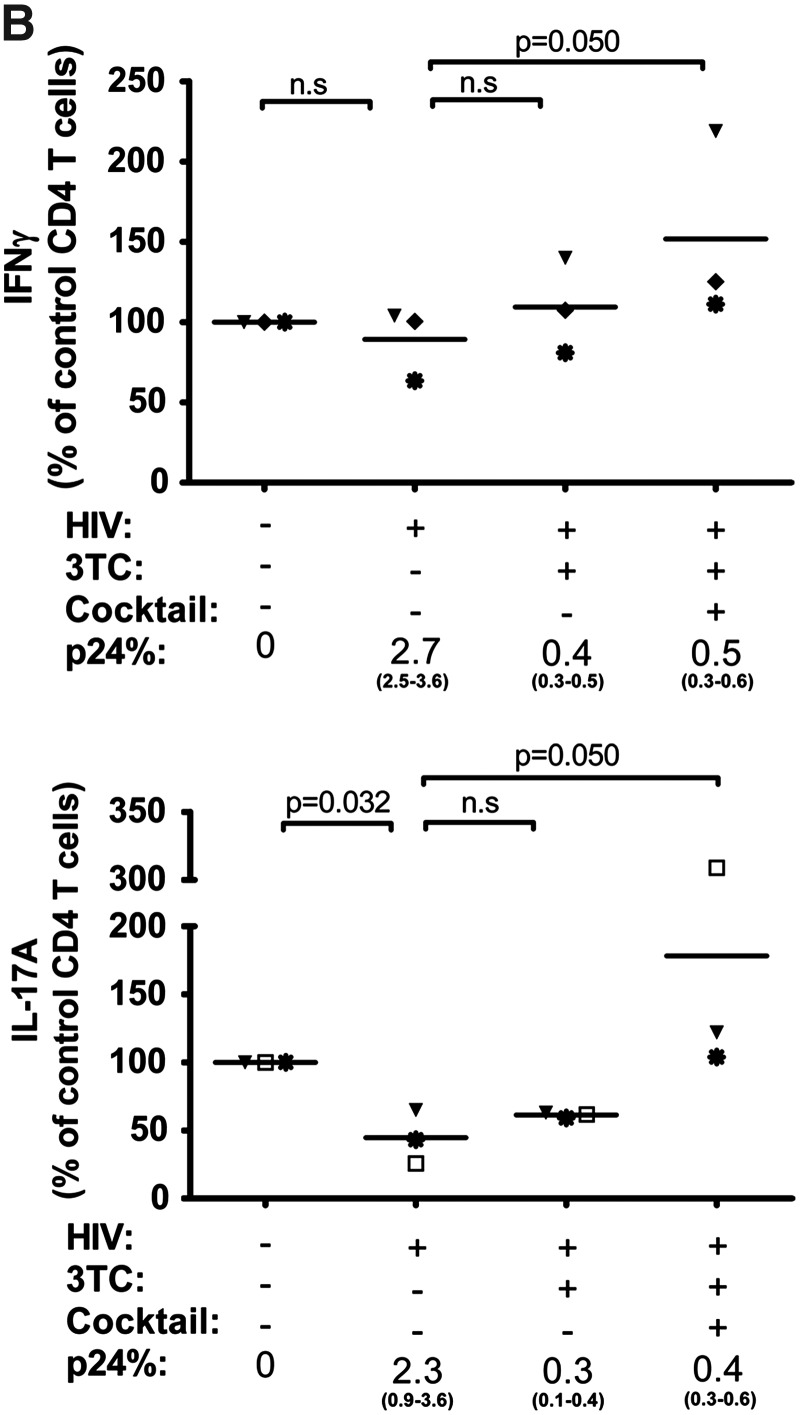
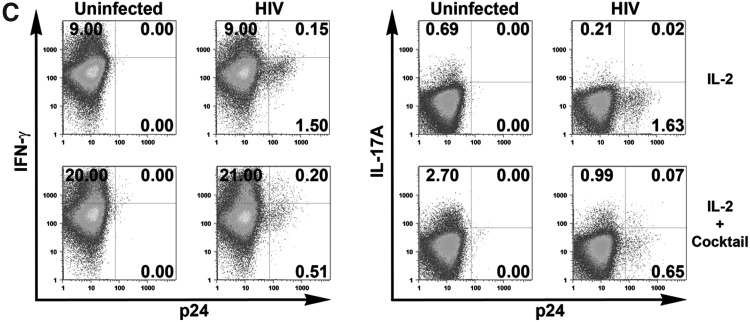
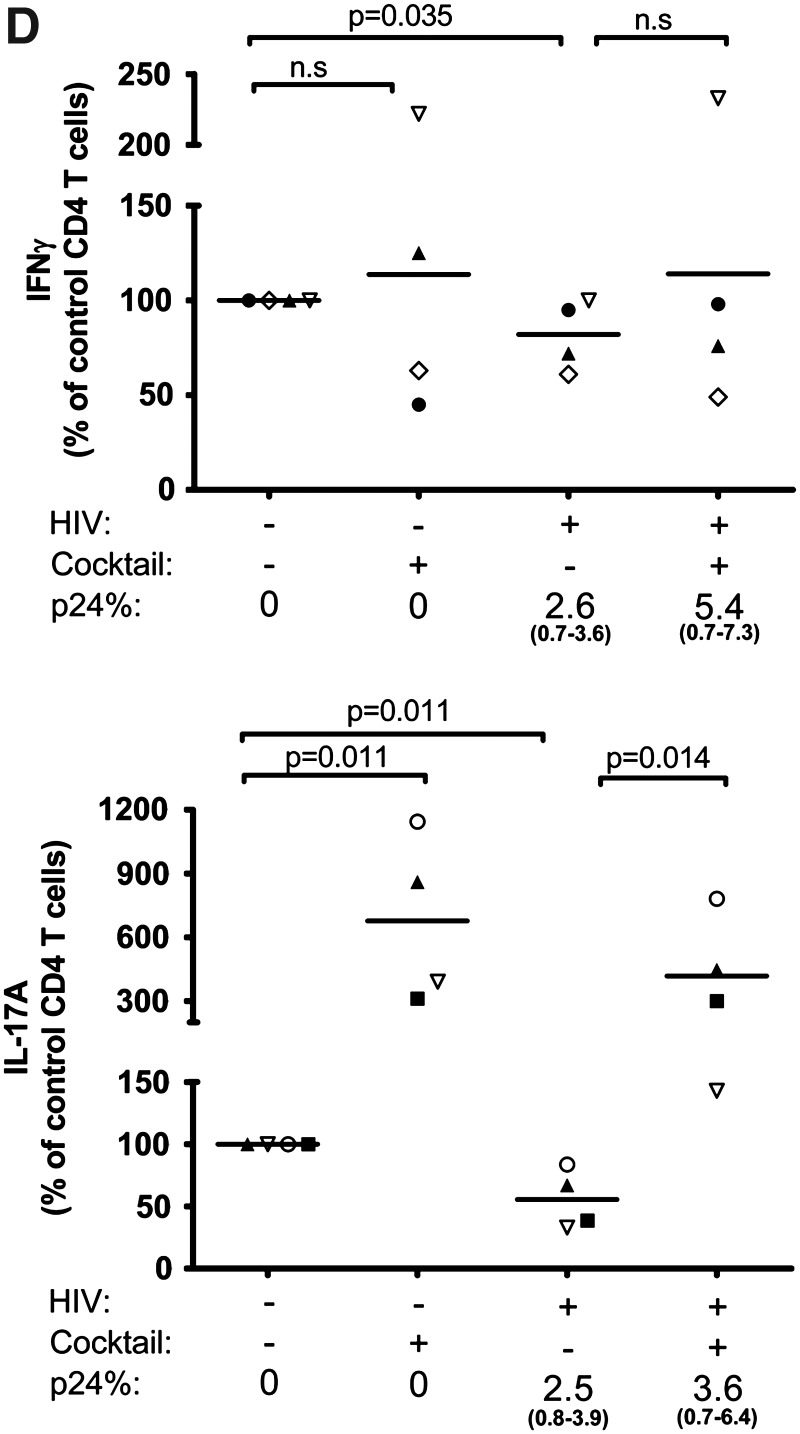
FIG. 4.
Expansion of the Th17 response after the establishment of HIV infection by 3TC and Th17 differentiation cytokines. Isolated CD4 T cells were infected with HIV-1 97ZA009 for 4 days, then washed and treated with 3TC in the presence or absence of Th17 differentiation cytokines (IL-1β, TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-23) for 6 more days. Cells were restimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 6 h, and IFN-γ and IL-17A production was measured by intracellular cytokine staining. (A) Dot plots of CD4 T cells positive for p24 and IFN-γ or IL-17A from one representative donor are shown. (B) Summary of the relative changes in IFN-γ+ or IL-17A+ CD4 T cell frequencies in the designated cultures from each of three donors tested. (C, D) Effects of Th17 differentiation cytokines on Th1 and Th17 responses in uninfected and infected cultures in the absence of 3TC. CD4 T cell cultures treated with IL-2 alone or IL-2 and the Th17 differentiation cytokines (IL-1β, TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-23) were left uninfected or infected with HIV for 8 days. Cells were then stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 6 h, and stained for intracellular p24, IFN-γ, and IL-17A. Dot plots of IFN-γ+ and IL-17A+ CD4 T cells from one donor under the different culture conditions are shown (C). (D) Graphs depict changes of IFN-γ+ and IL-17A+ CD4 T cell responses in cultures from each of four donors tested. The percentages of CD4 T cells producing IFN-γ or IL-17A in uninfected cultures with no cytokine cocktail are normalized to 100%. p24% indicates the average and range of the percentages of p24+ CD4 T cells under the different experimental conditions. Statistical significance was determined with the exact Wilcoxon rank sum test.