Figure 8.
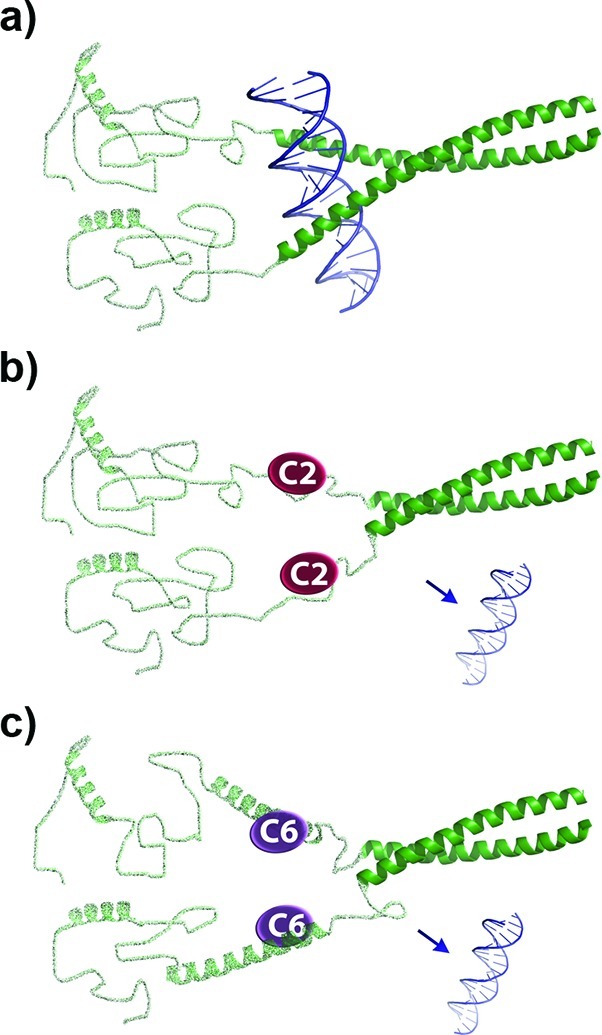
Possible mechanisms of action for C2 and C6. (a) In solution the N-terminus of ΔFosB is mostly unstructured. The C-terminal leucine zipper mediates dimer formation, while the preceding basic region adopts a helical conformation that interacts with DNA. (b) C2 likely binds to the DNA binding region, and thus blocks ΔFosB from binding DNA. (c) C6 likely binds to a region N-terminal to the basic region, inducing helical content to ΔFosB that prevents ΔFosB from undergoing conformational changes required for it to bind to DNA.
