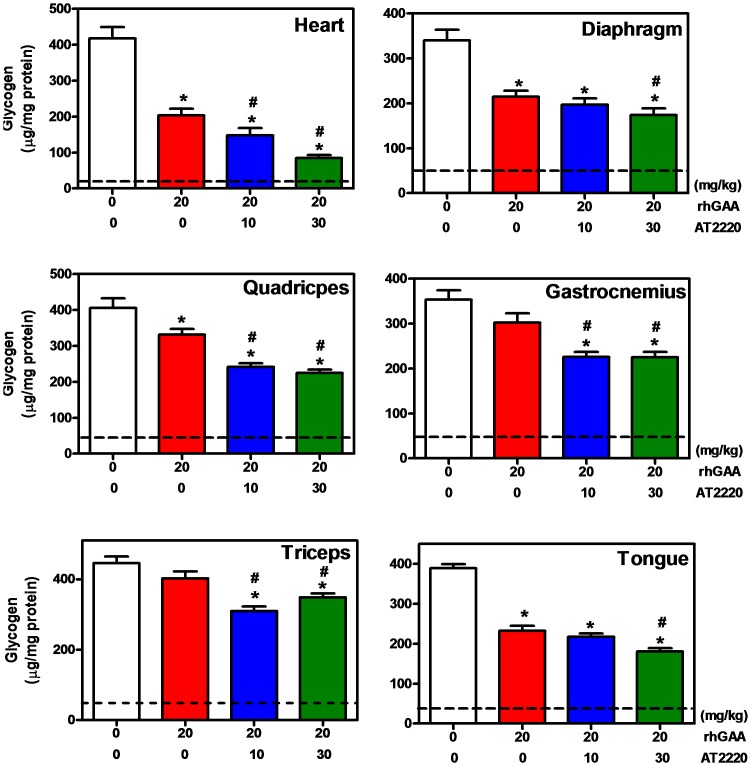
Figure 5. Co-administration of AT2220 promotes greater tissue glycogen reduction in GAA KO mice.
Twelve-week old male GAA KO mice were administered vehicle (water) or AT2220 (10 or 30 mg/kg) via oral gavage once every other week for 8 weeks. Thirty minutes after each AT2220 administration, vehicle (saline) or rhGAA (20 mg/kg) was administered via bolus tail vein injection. Mice were euthanized 21 days after the last (i.e., 4th) rhGAA administration and tissue glycogen levels were measured as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. Dotted lines show glycogen levels in the respective tissues of wild-type C57BL/6 mice. The data presented are an average of two independent studies with each bar representing the mean±SEM of the activity measured from 12 mice per group. Statistically significant reductions were seen in glycogen levels compared to baseline (*p<0.05, t-test) and compared to rhGAA administration alone (#p<0.05, t-test). In addition, the effect of AT2220 co-administration was also found to be significant for a linear trend (p<0.05; except in triceps), indicating a dose-dependent effect.