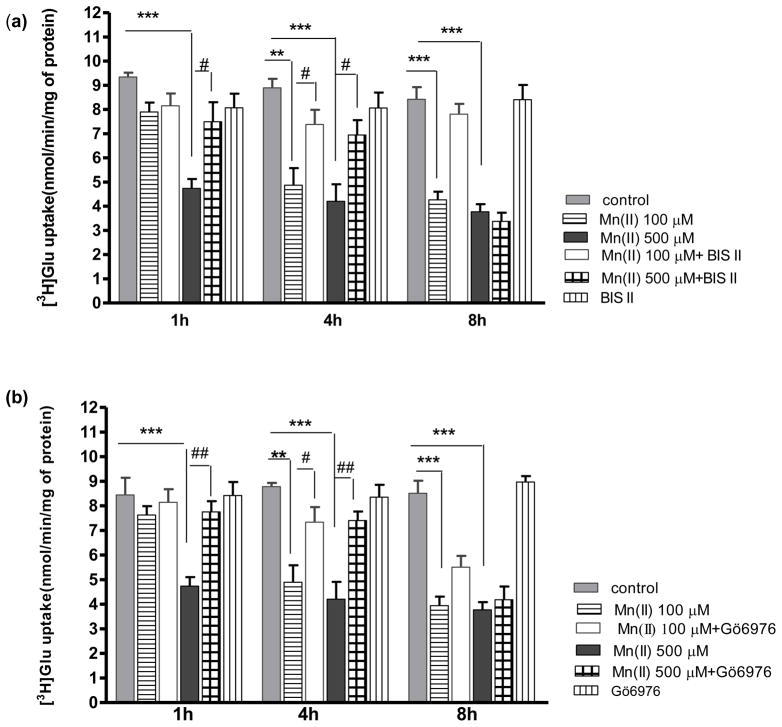
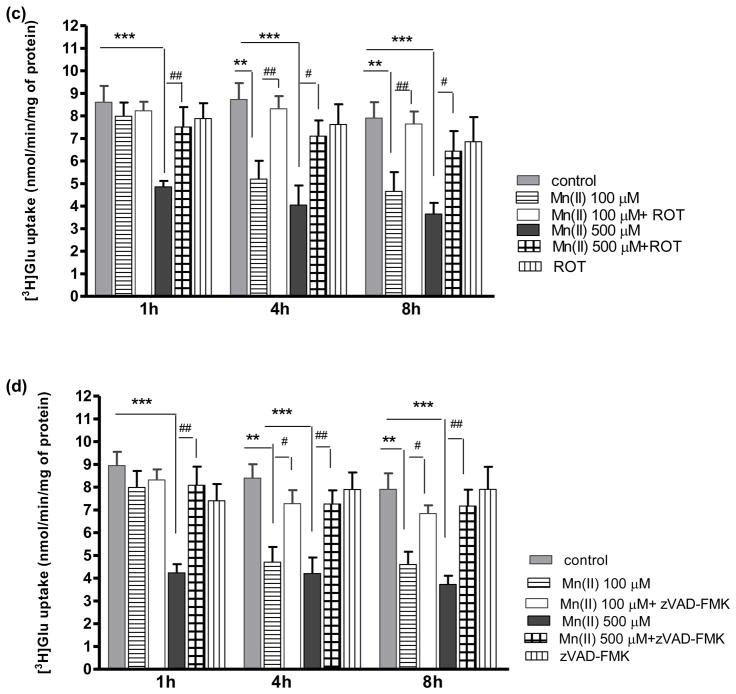
Fig. 3. Effect of PKC inhibition on Mn(II)-induced downregulation of astrocytic Glu uptake.
Total L-(G-3H)-Gln (0.25 μCi, specific activity: 49.0 Ci/mmol) uptake was measured after 1, 4 or 8 h exposure to 100 μM or 500 μM of Mn(II) alone or in presence of the general PKC inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide II (BIS II), two -way ANOVA found main effect of Mn(II) exposure ((F(1,103)=54.62, p<0.0001), Mn(II) x time interaction ((F(1, 103)=22.33, p<0.05) and Mn(II) x BIS II interaction ((F(1, 103)=15.099, p<0.0002) on Glu uptake (a); the selective PKCα inhibitor Gö6976, two -way ANOVA found main effect of Mn(II) exposure ((F(1,104)=73.60, p<0.0001), Mn(II) x time interaction ((F(1, 73)=62.13, p<0.05) and Mn(II) x Gö6976 interaction ((F(1, 103)=8.153, p<0.0052) on Glu uptake (b); the selective PKCδ inhibitor Rottlerin (ROT), two- way ANOVA found main effect of Mn(II) exposure ((F(1,87)=14.18, p<0.0002), Mn(II) x time interaction ((F(1, 93)=42.23, p<0.05) and Mn(II) x ROT interaction ((F(1, 87)=17.18, p<0.0001) on Glu uptake (c); the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (Z-Ala-Glu(OMe)-Val-Asp(OMe)-fluoromethyl ketone), two -way ANOVA found main effect of Mn(II) exposure ((F(1,101)=20.69, p<0.0001), Mn(II) x time interaction ((F(1, 77)=46.24, p<0.05) and Mn(II) x zVAD-FMK interaction ((F(1, 101)=26.80, p<0.0001) on Glu uptake (d). Data represent the mean ± S.D. from 4–5 independent sets of cultures, each performed in triplicate; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. Mn(II) exposed cells (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test).