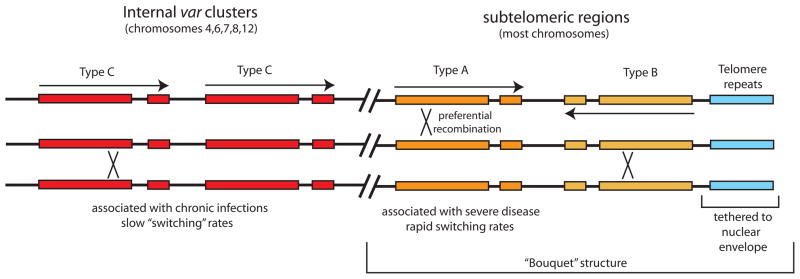
Figure 1.
Arrangement of var genes within the P. falciparum genome. There are ~60 var genes found in the parasite’s genome, divided into three basic types, A (yellow), B (orange) and C (red). Type B genes are typically found immediately adjacent to the telomeric repeats (blue) and transcribed away from the telomere. Type A genes are usually also found within the subtelomeric domains, but transcribed toward the telomeres. Type C genes are located in tandem arrays in the central regions of chromosomes 4,6,7,8 and 12. The telomeres are tethered to the nuclear envelope and are gathered into clusters of 6–8 telomere within a “bouquet” structure that results in physical alignment of the Type A and B genes. This alignment is proposed to aid in preferential recombination between genes of the same type. A similar structure may also contribute to recombination between Type C genes.