Figure 6.
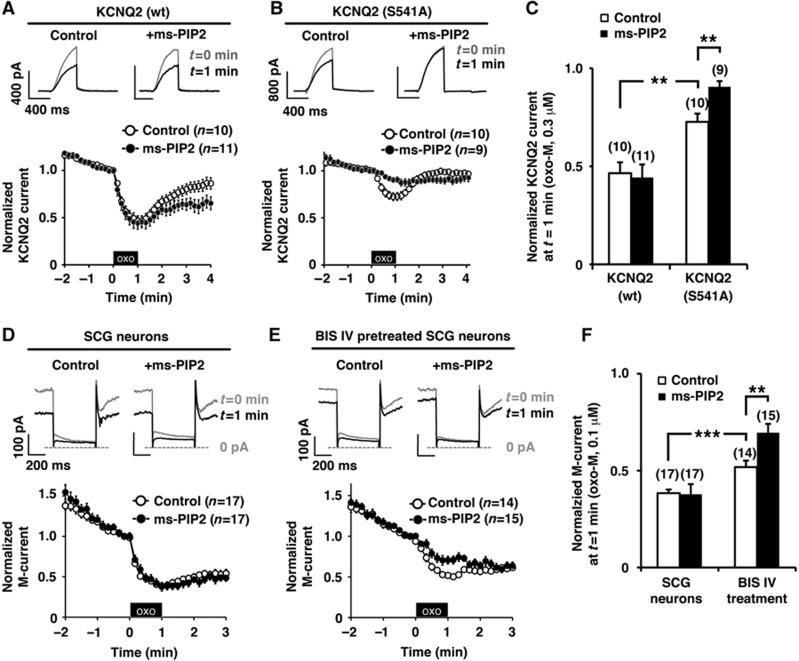
PKC phosphorylation sensitizes KCNQ2 channel and M-channel for reduction of PIP2 during muscarinic stimulation. (A) A PLC-resistant PIP2 analogue, ms-PIP2, did not disrupt oxo-M responses of wild-type KCNQ2 channel recorded by whole-cell patch clamp. The black box indicates the presence of 0.3 μM oxo-M. (B) Ms-PIP2 disrupted oxo-M responses of KCNQ2 (S541A) channel. (C) Pooled data of normalized KCNQ2 current at t=1 min from (A, B) showing that exogenous ms-PIP2 had no effects on wild-type KCNQ2 channel in response to oxo-M. But for KCNQ2 (S541A) channel, ms-PIP2 attenuated the oxo-M response. **<0.01 by nonparametric ANOVA followed by t-test. (D) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of the M-current from SCG neurons showing muscarinic suppression. Ms-PIP2 did not change the oxo-M response of the M-current. (E) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of the M-current from SCG neurons after pretreatment with 10 μM BIS IV. BIS IV treatment attenuated 0.1 μM oxo-M response, which was further suppressed by ms-PIP2. (F) Pooled data showing that exogenous ms-PIP2 attenuated oxo-M response when combined with BIS IV treatment. **<0.01, ***<0.001 by nonparametric ANOVA followed by t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m.