Table 4.
Covariate, inter-individual variability, and residual error relationships considered during model building
| Mathematical function | Compounds tested | |
|---|---|---|
| Covariate relationshipa | ||
| Continuous covariate | ||
| No relationship |
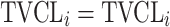
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Additive |
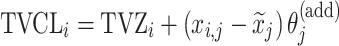
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Olanzapine, Perphenazine |
| Proportional |
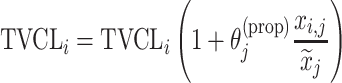
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine |
| Exponential |
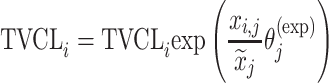
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Olanzapine, Ziprasidone |
| Power-law |
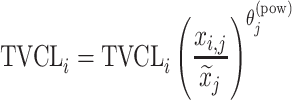
|
Citalopram, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine |
| Michaelis–Menten |
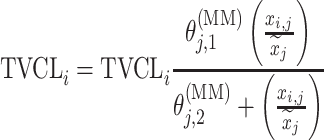
|
DMAG |
| Discrete | ||
| No relationship |
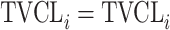
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Additive |
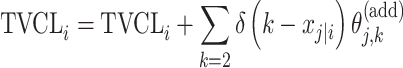
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Ziprasidone |
| Proportional |
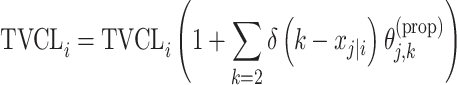
|
Perphenazine |
| Exponential |

|
Risperidone, Perphenazine |
| Type of inter-individual variabilityb | ||
| No relationship |
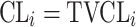
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Exponential |
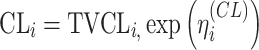
|
Citalopram, DMAG,Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Type of residual variabilityc | ||
| Additive |
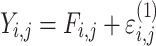
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Proportional |
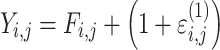
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
| Combined additive and proportional |
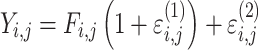
|
Citalopram, DMAG, Escitalopram, Olanzapine, Perphenazine, Risperidone, Ziprasidone |
aModification of a typical value for the example of clearance of the ith individual by the jth covariate or where x
i,j is the value of the jth covariate for the ith patient, 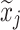 is the median value of the jth covariate,
is the median value of the jth covariate, 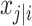 is the category (counting) number of the jth covariate for the ith patient, and
is the category (counting) number of the jth covariate for the ith patient, and  is a parameter for functional form n that describe the relationship of the jth covariate
is a parameter for functional form n that describe the relationship of the jth covariate
bInter-individual function forms considered for the example of the clearance of the ith individual. The 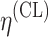 takes a standard normal distribution with standard deviation
takes a standard normal distribution with standard deviation 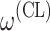
cResidual variability function forms considered. The variable Y
i,j is the jth observation for the ith patient, F
i,j is the corresponding model prediction, and 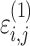 and
and 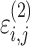 take standard normal distributions with variances
take standard normal distributions with variances 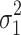 and
and 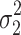 , respectively
, respectively
