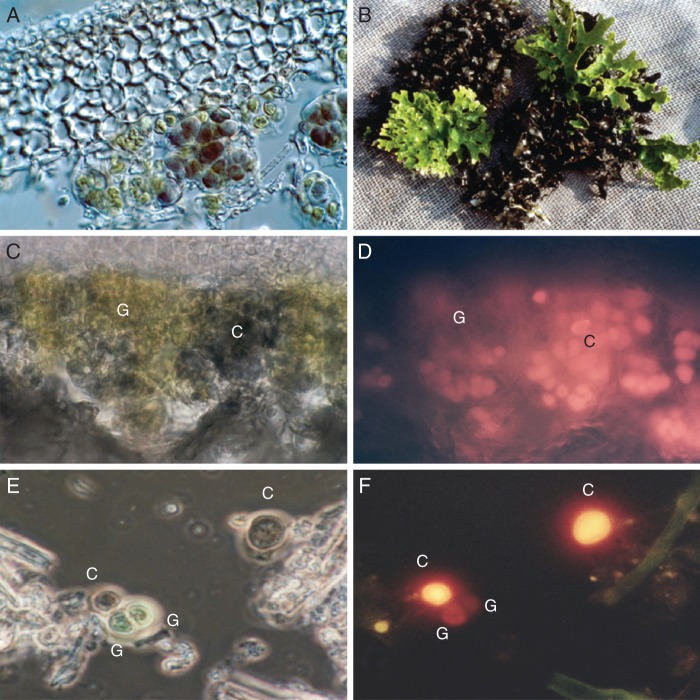
Fig. 1.
(A) Photomicrograph (DIC; Nomarski mode) of a vertical section through a thallus of the cyanobacterial lichen Ps. rufovirescens/cyan showing the green algae (green colour, left, lower centre) and cyanobacteria (dark colour, lower centre and right centre) beneath the upper cortex. (B) Thallus of a Ps. rufovirescens photosymbiodeme composed of sectors that are green algal (bright green colour) and cyanobacterial (dark colour). (C) Photomicrograph under normal light of a thick vertical section through a thallus of the cyanobacterial lichen Ps. rufovirescens/cyan; the green areas, G, are green algae and the darker areas, C, are cyanobacteria. (D) As in (C) but in fluorescence mode with green excitation light; only the cyanobacterial cells, C, fluoresce bright yellow/orange. (E) Photomicrograph under normal light of isolated photobionts from the cyanobacterial lichen Ps. rufovirescens/cyan; the labels C indicate cyanobacterial cells and G indicate green algal cells. (F) as in (E) but in fluorescence mode under green excitation light; the cyanobacterial cells fluoresce bright yellow/orange and the green algal cell shows almost no fluorescence.