Figure 1.
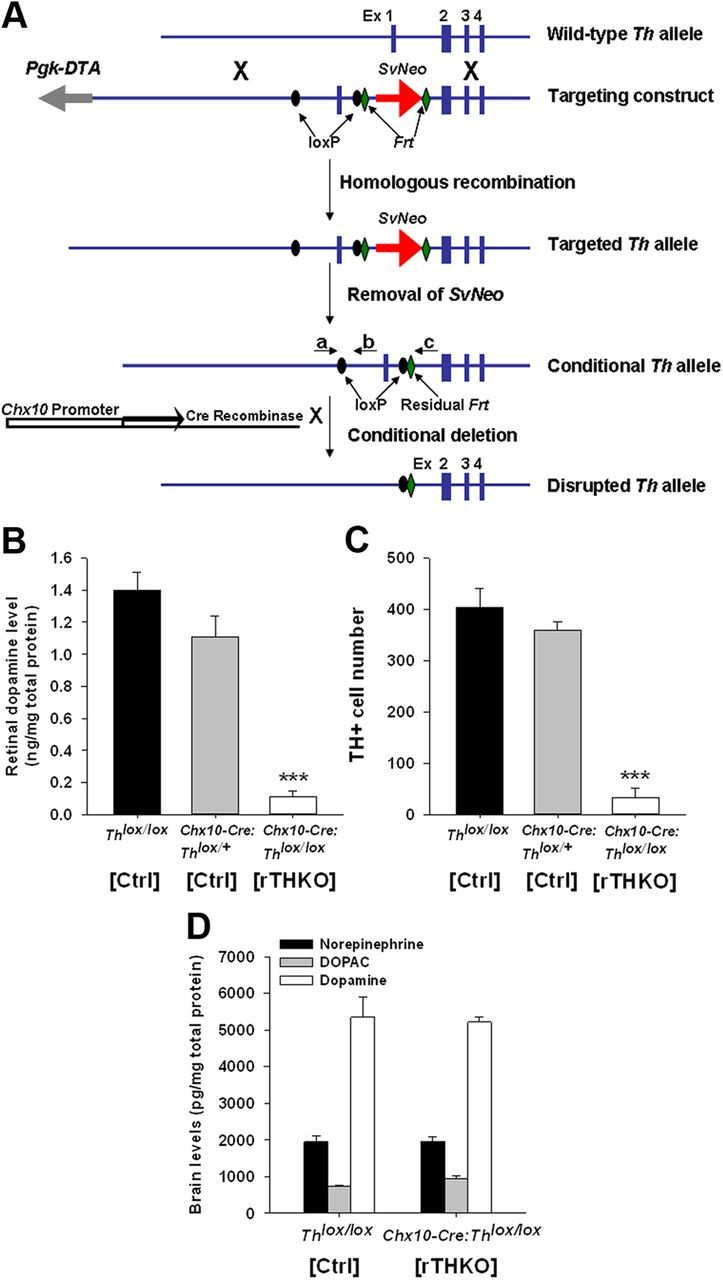
Generation of retina-specific Th knock-out mice. A, Generation of conditional Th mice. Blue boxes, exons (Ex); gray arrow, negative selection marker Pgk-DTA; red arrow, neomycin resistance gene under the control of the Sv40 promoter (SvNeo); black ovals, loxP sites; green diamonds, Frt sites; black arrows depict Cre recombinase under the control of the Chx10 promoter (white box). Primers a plus b amplify 150 bp for the WT Th allele and 200 bp for the Thlox allele, while primers a plus c yield a single ∼1000 bp band for homozygous mice, a single ∼900 bp band for WT mice, and two bands for hemizygous mice. B, Retinal dopamine levels in Ctrl (Thlox/lox), hemizygous-Ctrl (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/+), and homozygous-rTHKO mice (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/lox) as measured by HPLC. HPLC was performed as described by (Ruan et al., 2008). Data are represented as means ± SEM (n = 4). C, TH-immunoreactive (TH+) cell number in the Ctrl (Thlox/lox), Ctrl (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/+), and rTHKO (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/lox) mouse retinas. Immunocytochemistry was performed as described by (Ruan et al., 2008). Data are represented as means ± SEM (***p < 0.01, n = 4 mice). D, Brain dopamine (white bars), DOPAC (gray bars), and norepinephrine (black bars) levels measured in Ctrl (Thlox/lox), Ctrl (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/+), and rTHKO (Chx10-Cre:Thlox/lox) by HPLC; no significant change.
