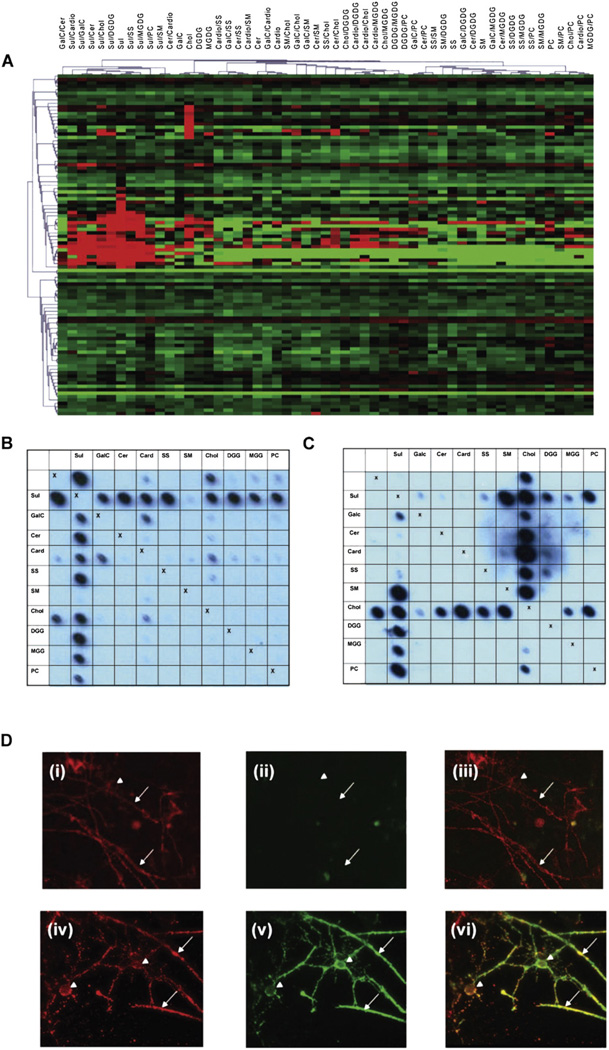
Fig. 3.
Array analyses for rAbs. (A) Heat map depicting reactivity of rAbs derived from MS and OND patient CSF. The lipid antigens are displayed as column headings and each row represents an individual rAb. Table 2 lists the sources of MS and control rAbs and more detailed analyses of individual rAbs can be found in Owens et al. (2009) and Bennett et al. (2009). Covariance clustering of all rAb reactivities has been performed revealing two populations of lipid reactive antibodies; one directed against sulfatide or sulfatide/lipid complexes and the other against cholesterol. MS rAbs do not segregate with unique binding profiles, as lipid reactivities are also seen in OND rAbs (19% V 37%). (B) Blot of the MS derived rAb 76. Note antibody binding to sulfatide is virtually abolished in the presence of sphingomyelin. (C) Blot of the mAb O4. In contrast to rAb 76, binding to sulfatide is enhanced not inhibited by sphingomyelin. (D) Unfixed myelinating cultures derived from embryonic rat spinal cord were stained at 4 °C with either (D) (i)–(iii) MS derived rAb 76 (10 µg/ml) or (D) (iv)–(vi) mAb O4 (10 µg/ml) to visualize sulfatide (green) and the MOG-specific mAb Z2 (10 µg/ml) to identify oligodendrocytes and myelin sheaths (red). After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde bound antibody were detected using species-specific secondary reagents (anti-human — green; anti-mouse — red). Control cultures were stained with polyclonal human IgG, mouse myeloma proteins and/or secondary antibodies alone. In no case did immunoreactivity for MOG (red) at the surface of oligodendrocytes (arrow head) or myelinated internodes (small arrows) co-localize with bound human rAb ((ii), green) as demonstrated in the merged image (iii). Staining obtained using this and other rAbs was restricted to a diffuse background indistinguishable from that observed when cultures were stained using polyclonal human IgG pooled from multiple donors. In contrast the sulfatide reactive mAb O4 binds the surface of oligodendrocytes and myelin sheaths where it co-localizes with the MOG-specific mAb Z2 (iv)–(vi). This marked difference in immunoreactivity of sulfatide reactive rAbs and mAb O4 is associated with marked differences in recognition of lipid complexes using lipid arrays.