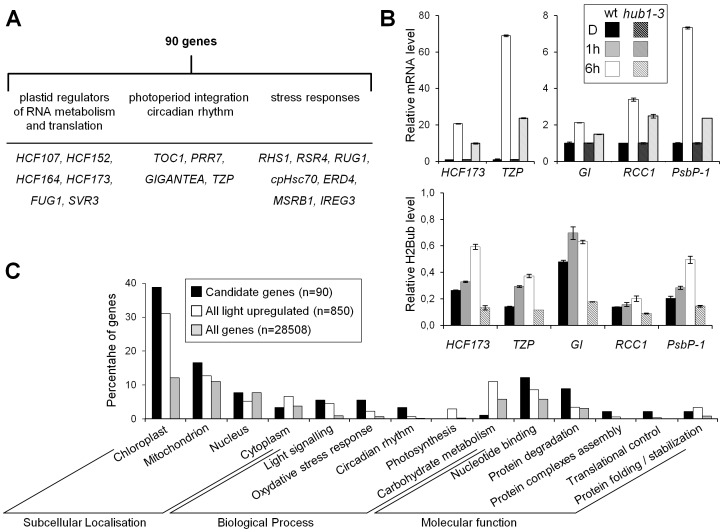
Figure 7. Several genes potentially targeted for H2Bub selective regulation encode regulatory factors of light-driven responses.
(A) Candidate genes for H2Bub selective regulation. (B) Experimental validation of the selection criteria for HCF173, TZP, GIGANTEA (GI), RCC1 and PsbP-1 genes. RT-qPCR (upper panels) and ChIP-qPCR (lower panels) analyses show weak upregulation in the hub1-3 mutant and H2Bub enrichment in the wild-type upon 6 h of illumination. RNA levels at 6 h are given relative to the dark sample (arbitrarily set to 1) and after normalization against At4g29130 and At2g36060 housekeeping genes. For ChIP analyses, levels are given as in Figure 3C as percentages of IP/Input relative to the mean signals of two control genes (At4g23100 and At4g22330) and normalization to nucleosome occupancy determined by anti-H3 ChIPs. Error bars represent standard deviations from two replicates. The hub1-3 mutant serves as a control for antibody specificity. (C) Selected categories of Gene Ontology for the 90 candidates showing the over-representation of DNA-binding proteins, circadian clock components, and proteins involved in translational control, while components of the photosynthetic apparatus are under-represented.