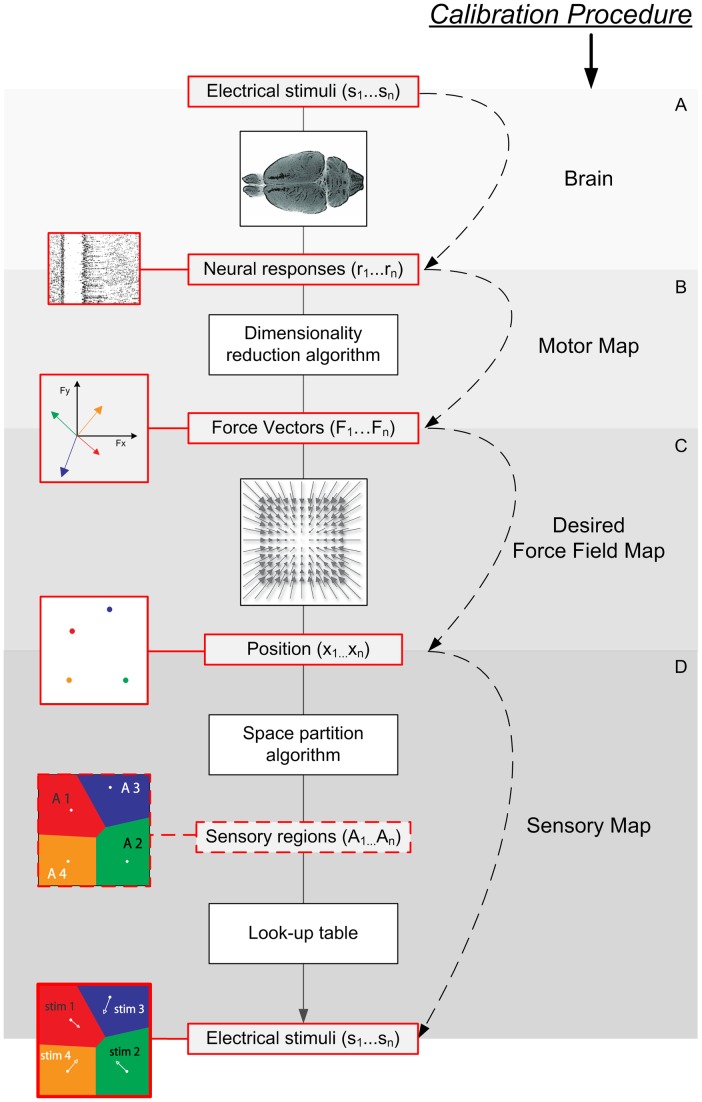
Figure 2. Calibration procedure scheme.
The purpose of the calibration procedure is to set the parameters of the neural interface. The calibration consists of 4 steps. (A) Recording a training set. The calibration procedure is performed upon a training set (r1…rn) built by recording the neural activities evoked over multiple presentations (usually 100) of each of the n stimulation patterns (s1…sn with n = 4 in this example). (B) Motor Map. The training set is also used to set the motor map. The spike trains from multiple neurons are reduced by PCA to two coordinates of a force vector. In this example the result of this operation is a set of 4 template vectors, each corresponding to a stimulation pattern. (C) Desired force field map. The chosen desired force field to be approximated (e.g. a continuous radial force field converging towards a central equilibrium point) establishes a relationship between the n template vectors and the n positions in the two-dimensional space. (D) Sensory Map. The n positions are used to partition the external device space by using a space partition algorithm (e.g. in this case a nearest neighbor map) and, as a consequence, n sensory regions (A1…An) are defined. A look-up table connects each sensory region to a corresponding stimulation pattern. As a result, the sensory map converts each position of the space into a stimulation pattern.