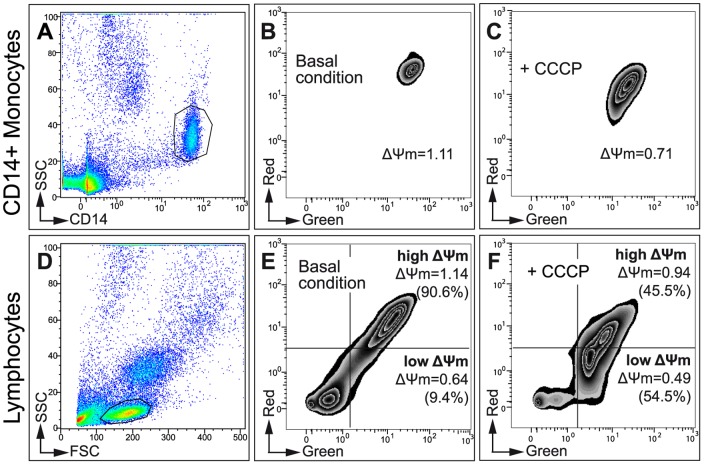
Figure 2. Determination of mitochondrial inner membrane potential (ΔΨm) in lymphocytes and monocytes.
JC-1 is a cationic carbocyanine probe that exibits a potential-dependent accumulation in mitochondria as either a monomer at low concentrations (green fluorescence) or as aggregates at higher concentrations (red fluorescence) [28]. Therefore, the red/green fluorescence intensity ratio illustrates ΔΨm. (A to C) Monocytes. (A) CD14+/SSC monocyte gating. (B) Representative zebra plot based on side scatter and ΔΨm. (C) Representative zebra plot based on side scatter and ΔΨm after inhibition of ΔΨm with CCCP (control experiment). (D to F) Lymphocytes. (D) FSC/SSC lymphocyte gating. (E) Representative zebra plot based on side scatter and ΔΨm. Two lymphocyte subpopulations were distinguished (low-ΔΨm, bottom right quadrants; high-ΔΨm, top right quadrants). The top and bottom right quadrants indicate the ΔΨm mean values (cell percentages). The percentages of low-ΔΨm lymphocytes were: Control: 14.7±8.2%; ART naive: 12.56±4.4% (statistically different from control); 2NRTI+1PI/r: 17.0±8.4%; 2NRTI+1NNRTI: 15.3±7.3%; 3NRTI: 16.3±5.1%. (F) Representative zebra plot based on side scatter and ΔΨm after inhibition of ΔΨm with CCCP (control experiment).