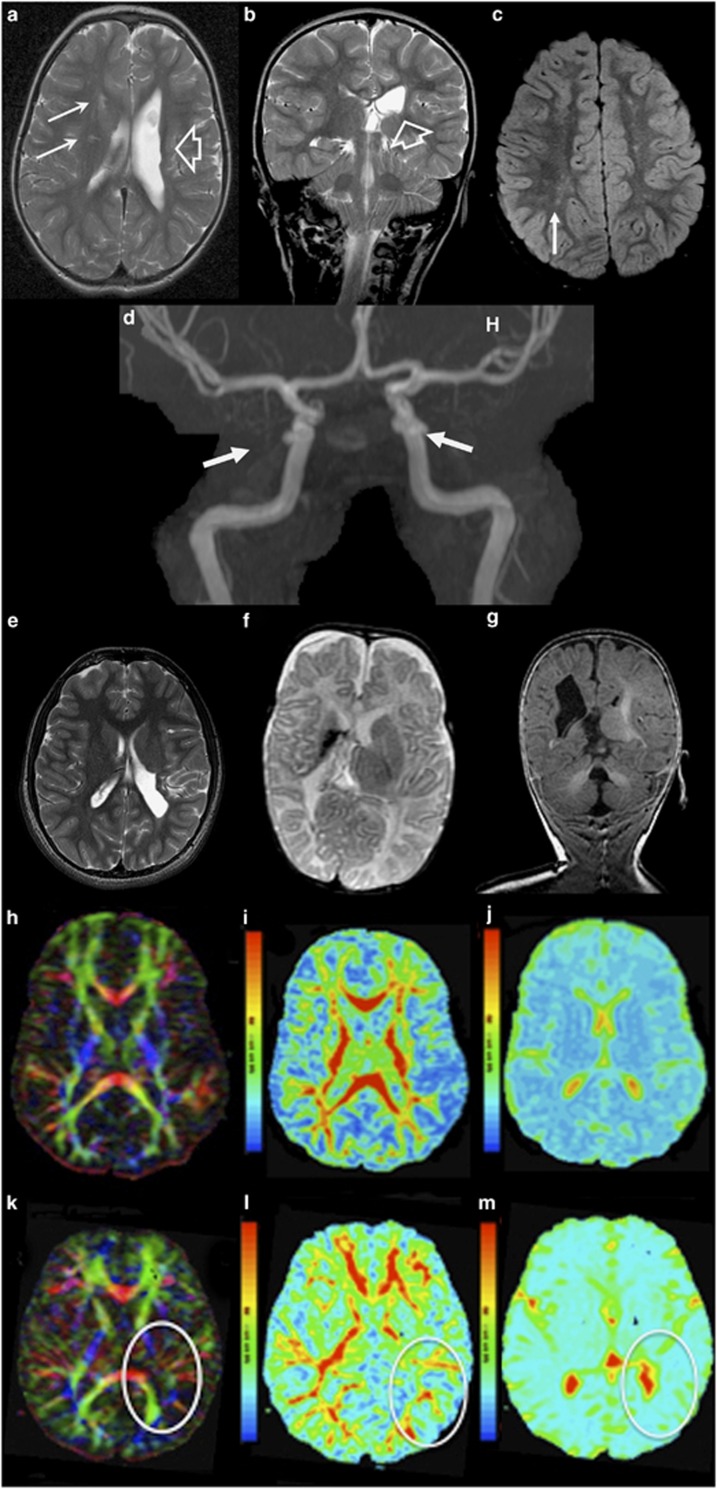
Figure 2.
Brain MRI of patients with COL4A2 mutations. (a, b) Axial and coronal T2 of patient III.2 from family A at the age of 2 years indicate ex-vacuo dilation of the left lateral ventricle (porencephaly) (open arrow) and periventricular white matter lesions (solid arrows) resulting from presumed perinatal stroke. (c) FLAIR image illustrates T2 prolongation in the white matter – in patient III.1 from family A at the age of 8 years, suggesting gliosis (arrow). (d) MR angiography of their mother (subject II.1, family A) at adult age shows bilateral internal carotid aneurysms (at the level of cavernous sinus). (e) Axial T2 weighted images of Patient II.2, family B, at the age of 15 years show a porencephalic dilatation of the left occipital ventricle. (f, g) Axial T2 weighted and coronal FLAIR images of patient II.5 from family B at the age of 5 months show porencephaly of the right ventricle with hypoplastic left cerebellar hemisphere. (h–m) Reconstruction of the white matter tracts obtained from magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging (MR-DTI) data. (k,l) Patient II-2 (family B) reveals reduced fractional anisotropy in the left radiation optica and tractus corticospinalis at the side of the porencephalic lesion (encircled), compared with an age-matched control (h,i). A restriction of the total ADC was observed in the whole cerebral white matter of the patient (m), compared with an age-matched control (j).