Figure 1.
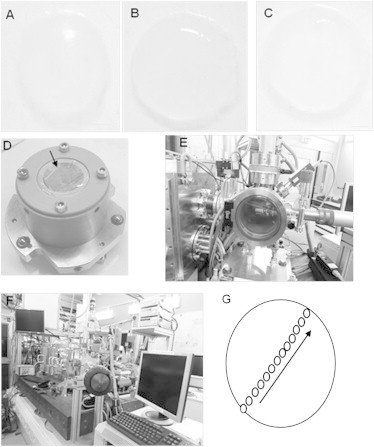
Sample preparation for acquisition of XRF and XANES spectra. (A) Dissected chick cornea at embryonic day 12, (B) day 14, and (C) day 16. (D) The sample is sandwiched between two sheets of ultralene foil and mounted on the sample holder. The arrow indicates the surface that will be exposed to the x-ray beam. (E) The Simulatore di Ambiente Spaziale (SAS) vacuum chamber for sample mounting. Once the sample is placed inside the SAS is pumped. When high vacuum is reached the sample can be introduced into the scanning x-ray microscope by means of a transfer cane. (F) Photograph of the scanning x-ray microscope at the end station ID 21, ESRF. Scale bar equals to 1 mm. (G) Diagram indicating from where the S speciation XANES point spectra for every developing chick cornea were obtained. For each sample spot, five XANES spectra were acquired. Black arrow shows the direction at which ∼13 points were selected to be analyzed.
