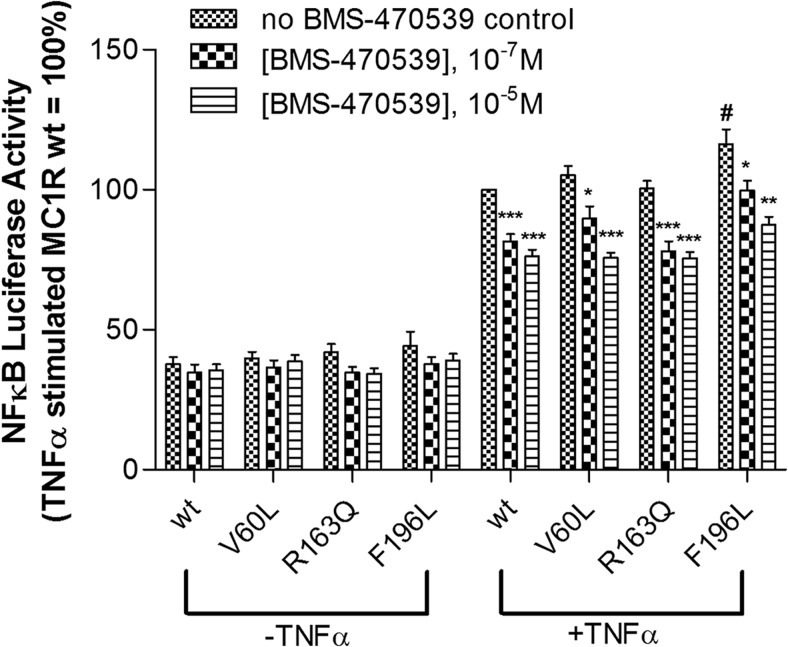
Fig. 9.
BMS-470539 inhibits TNFα-induced NFκβ activity in cells expressing wild-type or variant MC1Rs. In the presence of TNFα alone, the F196L variant shows an elevated level of NFκB-luciferase activity relative to wild type. A549 cells were transiently transfected with cDNA encoding the indicated receptors together with an NFκB-luciferase reporter gene construct. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were preincubated with or without BMS-470539 for 30 min, followed by further incubation in the presence of TNFα (0.5 ng/ml) for another 4 h. Luciferase activity was then determined as described under Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as a percentage of TNFα-stimulated NFκB-luciferase activity observed in cells expressing wild-type MC1R, in the absence of BMS-470539. Bars represent the mean ± S.E.M from at least four independent experiments. In the absence of TNFα stimulation, no significant differences were observed between wild-type and variant receptors (p > 0.05). Comparison of TNFα-stimulated NFκB activity versus wild-type receptor control in the absence of BMS-470539: #, p < 0.05. Comparison of NFκB activity at each receptor in the presence of increasing concentrations of BMS-470539: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.