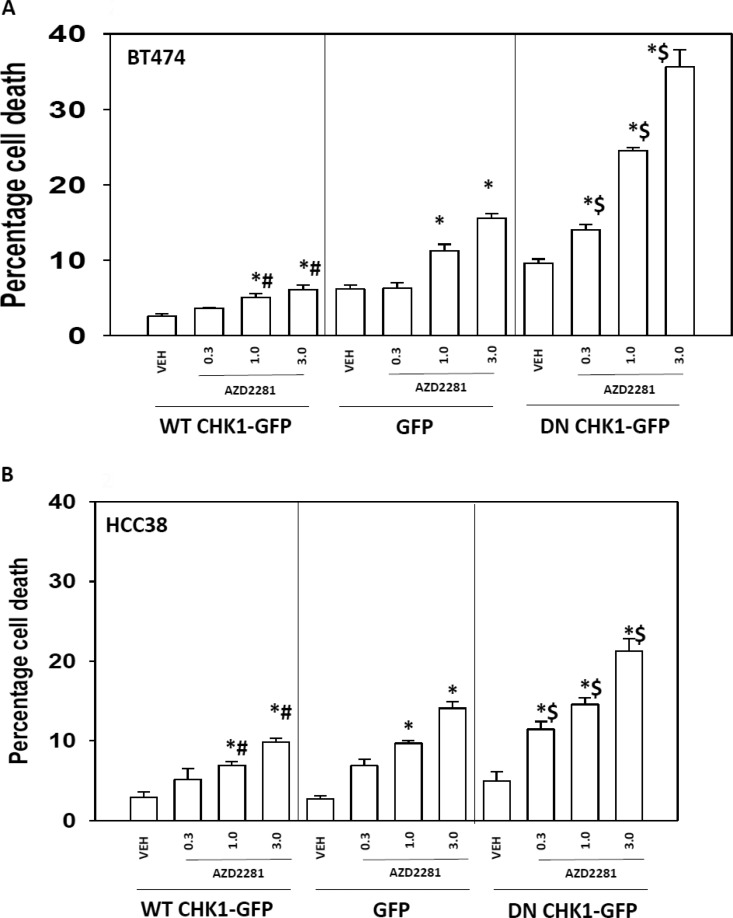
Fig. 2.
Dominant-negative Chk1 increased the sensitivity of the cells toward PARP inhibitor treatment. BT474 (A) or HCC38 (B) cells were transfected with WT CHK-GFP, dominant-negative (DN) CHK1-GFP, or GFP control vector. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were treated with the PARP1 inhibitor AZD2281 (0.3, 1, or 3 μM) for 48 h. Floating and attached cells were isolated after drug exposure, and cell viability was measured by trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). *, p < 0.05 greater than corresponding vehicle control; #, p < 0.05 less than corresponding value in GFP; $, p < 0.05 greater than corresponding value in GFP.