Figure 4.
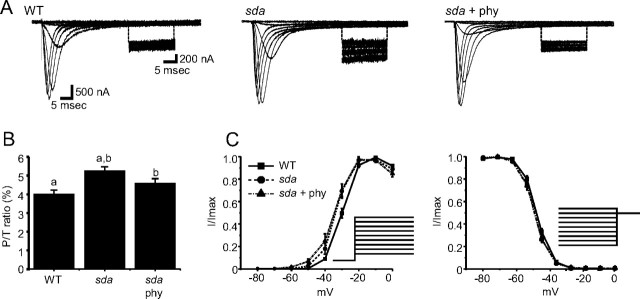
Altered splicing of DmNav in sda increases INap. A, Traces of INa recorded from heterologous expression of DmNav cRNA mixtures in Xenopus oocytes. Traces show currents evoked by Δ10 mV depolarizing voltage steps from a holding potential of −90 mV (full details are provided by Lin et al., 2009). Inset, For each trace, a section of INap is shown with a magnified amplitude. Expression of the sda DmNav mixture increases INap compared with WT. Expression of the DmNav mixture expressed in aCC isolated from larvae fed phenytoin (sda + phy) shows a reduced INap compared with that from sda alone. B, Average values for INap for the three DmNav cRNA mixtures expressed (for composition, see Table 3). Values shown are 4.0 ± 0.2, 5.3 ± 0.2, and 4.6 ± 0.2%, respectively (identical letters denote p ≤ 0.05, n ≥ 8). P/T ratio, Persistent/transient ratio. C, Voltage dependence of activation is significantly hyperpolarized in the sda and sda + phenytoin DmNav mixtures (p ≤ 0.05, n ≥ 8). D, Voltage dependence of inactivation is not significantly different between the three conditions (p > 0.05, n ≥ 8). Protocols for activation and inactivation are shown by Lin et al. (2009).