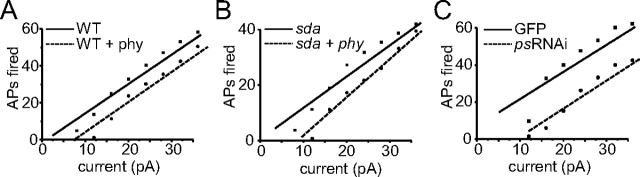
Figure 6.
Blocking INap reduces membrane excitability. A, Action potentials (APs) evoked by injection of constant depolarizing current (500 ms) in WT aCC are fewer in number in the presence of phenytoin (phy; 30 μm). B, This same dose of phenytoin also reduces action potential firing in sda aCC neurons. Note that sda neurons fire fewer action potentials than WT aCC even in the absence of phenytoin, an effect that is most likely attributable to synaptic homeostasis (Marley and Baines, 2011). C, Expression of ps RNAi in WT aCC neurons also results in a reduction in action potential firing compared with controls (GAL4RRa > UAS–GFP). Reduction of ps increases splicing of exon K and a smaller INap as a consequence (Lin et al., 2009). Values shown are averages from n ≥ 5.