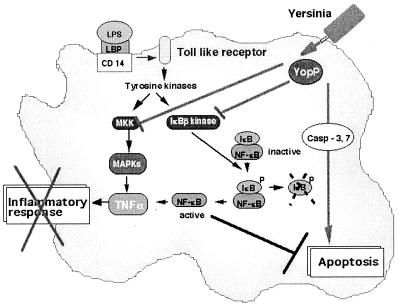
Figure 3.
Effects of YopP/YopJ. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bound to the LPS-binding protein (LBP), interacts with its receptor CD14 and coreceptor from the Toll-like family, which leads to phosphorylation cascades resulting in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and of the kinase of the inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB). Phosphorylation of IκB is followed by its degradation, and NF-κB migrates to the nucleus and activates transcription of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α. Translocated YopP/YopJ prevents the activation of the two phosphorylation cascades, and thus blocks the release of TNF-α. YopP/YopJ also induces macrophage apoptosis. See text for details and references.