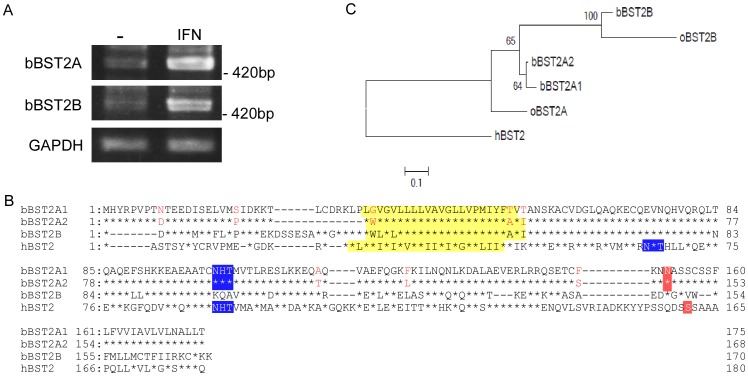
Figure 1. Deduced amino acid sequences of bovine BST-2s.
(A) RT-PCR was carried out for RNA extracted from MDBK cells treated with or without IFN-α, using a primer set specific for bBST-2A or bBST-2B, respectively. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of bovine BST-2s, bBST-2A1, bBST-2A2 and bBST-2B, with human BST-2 (GenBank accession No. NM_004335). Asterisks show amino acid residues conserved in the BST-2A1 sequence, and bars indicate spaces. The predicted transmembrane domains (yellow), N-glycosylation sites (blue) and GPI-recognition motifs (red) are boxed. Posttranslational modifications were predicted using the TMHMM Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM), the NetNglyc 1.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc) and the big-PI Predictor (http://mendel.imp.ac.at/gpi/gpi_server.html). (C) The maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of bBST-2s and human BST-2. The percent values were determined from 1000 repeats of fast bootstrapping using RAxML [34] are indicated at the branch junctions.