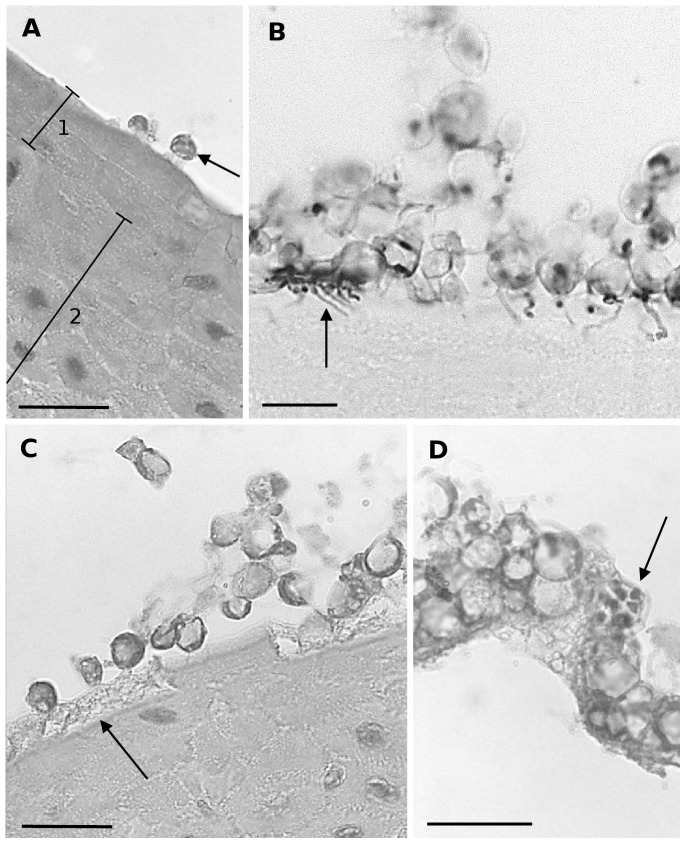
Figure 1. Light microscopical overview of the development of Bd in skin explants of Xenopus laevis.
(A) adhesion of encysted zoospores (arrow) to the host epidermis at 1 dpi; (1) stratum corneum, (2) stratum spinosum; haematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain; scale bar = 20 µm; (B) at 1 dpi Bd germlings have developed germ tubes, that penetrate the stratum corneum and develop into a branched mesh work of rhizoids (arrow) in heavily infected epidermis; Gomori methenamine silver stain; scale bar = 10 µm; (C) at 2 dpi the infected host cells have lost their cytoplasm (arrow) subsequent to invasion by Bd, only the cell membrane remains; HE stain; scale bar = 20 µm; (D) at 4 dpi germlings have developed into mature zoosporangia (arrow), the upper layer of the stratum corneum is shed; HE stain; scale bar = 20 µm.