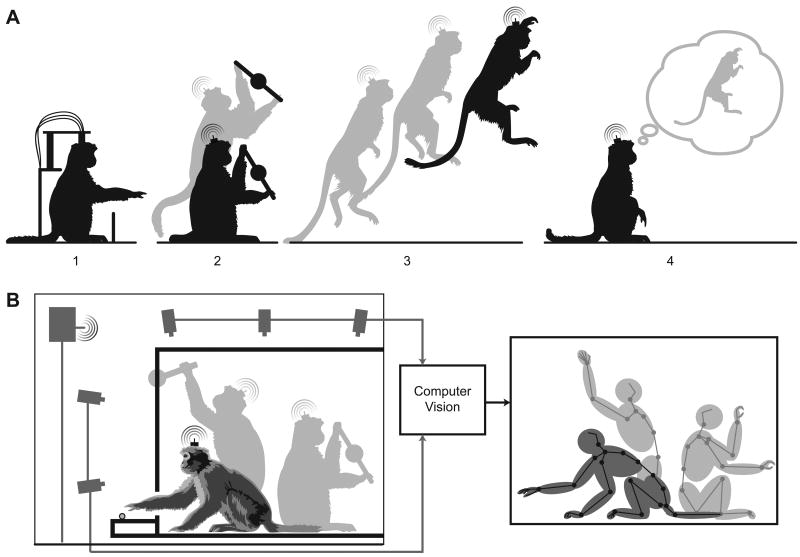
Figure 4.
Expanding the scope of motor system studies: (A) shows a progression of potential motor control studies enabled by head-mounted electrophysiology systems. 1 is the traditional wired in-rig setup in which the animal is engaged in a reaching task with a highly constrained posture. 2 utilizes a wireless telemetry system and the animal is able to move to many different postures as he plays with a sensorized manipulandam. 3 shows the possibility of studying complex movements, such as leaping. 4 is the ability to decode motor intentions. (B) is a sketch of a potential computer vision system for recording detailed body posture simultaneously with wireless neural data. The images from all cameras are used to construct a model of all joint positions at every moment in time.