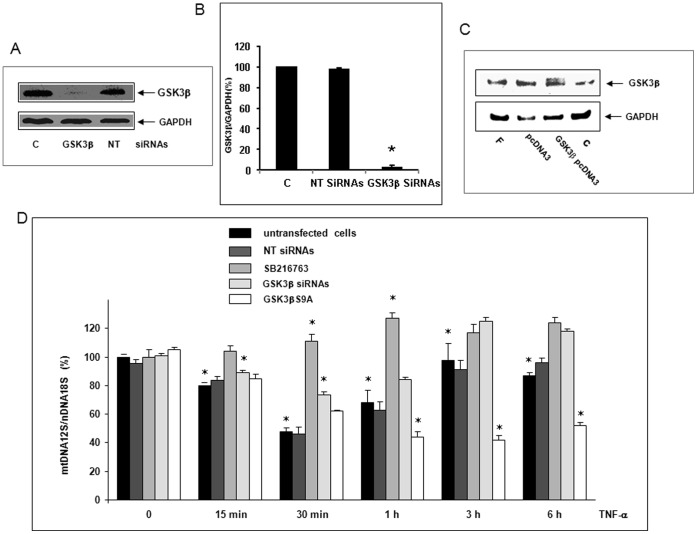
Figure 7. SB216763 or GSK3β siRNAs inhibited mtDNA depletion whereas GSK3βS9A suppressed the reversion.
(A) All siRNA transfections were performed or not (control, C) with 12.5 nM siRNAs directed against GSK3β mRNA (GSK3β siRNAs) or non-targeting (NT) siRNAs in DharmaFECT4® transfection reagent. To check SiRNA transfection efficiency, Western Blots were performed at 48 h with GSK3β or GAPDH (loading control) antibody. (B) Inhibition of GSK3β expression by siRNAs relative to GAPDH was quantified using the Bio1D software (mean values ± SEM of three experiments *p<0.05) (C) Cells were transfected or not (control C or Fugene HD® alone, F) with the mutant GSK3βS9A pcDNA3 plasmid or the empty plasmid (pcDNA3) using Fugene HD® (F). After 72 h transfection, the expression of recombinant GSK3βS9A protein was checked by Western Blot using GSK3β or GAPDH (loading control) antibody. (D) Cells were treated or not with SB216763 or transfected or not (untransfected cells) with NT siRNAs or GSK3β siRNAs or GSK3βS9A pcDNA3 plasmid. Then, they were treated for 0 (zero-time control) to 6 h with 30 ng/ml TNF-α. Total DNA was isolated and the quantification of mtDNA content performed by real-time qPCR co-amplification of fragments encoding mitochondrial 12S rRNA and nuclear 18S rRNA as a gene reference. Results are expressed in mtDNA over nDNA relative ratio (mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments with five replicates, *p<0.05).