Figure 1.
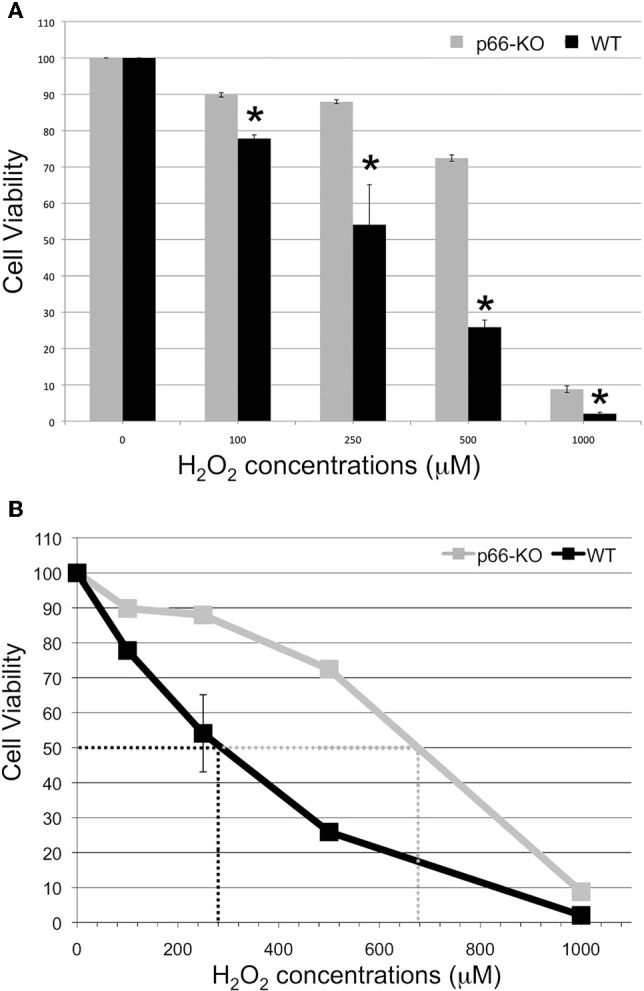
p66-KO neurons are more resistant to H2O2 treatment compared to WT neurons. Week-old p66-KO and WT hippocampal neurons were treated with various concentrations of H2O2 (100, 250, 500 μM, and 1 mM) for 15 min. Cell counts were obtained 24 h post-treatment using Calcein AM as a viability indicator. (A) Cell viability percentages were significantly greater for the p66-KO neurons compared to the WT neurons for the tested H2O2 concentrations (* = p < 0.05). (B) H2O2 concentration vs. survival percentage curves showed that the EC50 for 50% survival was approximately 280 μM for WT neurons and 680 μM for p66-KO neurons, demonstrating that p66 elimination is associated with increased resistance to H2O2 treatment (n per treatment/genotype = 3 cultures; 4 plates/culture).
