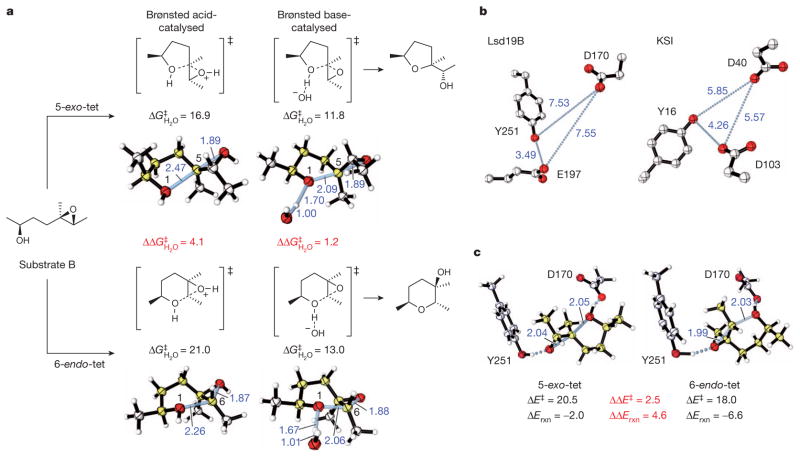
Figure 3. Computational studies of the Lsd19-catalysed epoxide-opening cyclization reactions.
a, Acid- versus base-catalysed cyclization of a model system via 5-exo or 6-endo cyclization, and the respective calculated lowest-energy competing transition structures. B2PLYP/6-311++G(d,p)//B2PLYP/ 6-31G(d) activation free energies (kcal mol−1) and forming/breaking bond distances (in Ångstroms, shown in blue) are given. b, Comparison of active-site geometries in Lsd19B and KSI (PDB accession 1E3V24). c, ‘Theozyme’ calculations, optimizing the competing 5-exo-tet and 6-endo-tet transition structures surrounded by fixed catalytic residues. Relative energies obtained by B2PLYP/6-311++G(d,p)/M06-2X/6-31G(d) (kcal mol−1) and forming/ breaking bond distances are given.