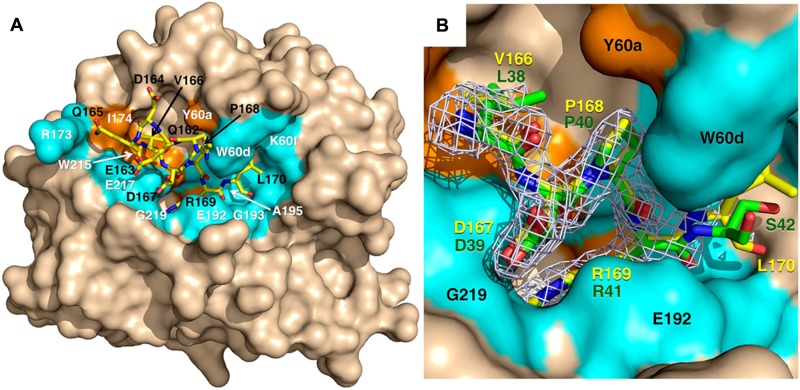
Figure 4.
X-ray crystal structure of thrombin S195A in complex with a fragment of the activation domain of protein C. (A) Thrombin is rendered in surface representation (wheat) with the active site in the center and exosite I on the right. The protein C peptide is rendered in stick representation (yellow). Residues of thrombin interacting with the protein C peptide through molecular contacts within 4 Å are in orange (hydrophobic contacts) or marine (polar contacts). (B) Details of how the P4 to P1′ residues of the protein C peptide (yellow sticks) dock into the active site of thrombin. The 2Fo-Fc electron density map (light green mesh) is contoured at 1 σ. A direct comparison is shown with the P4 to P1′ residues of the thrombin receptor PAR1 (green sticks).42 R169 penetrates the primary specificity pocket and is partially covered in this view by the side chain of E192. P168 at the P2 position makes strong hydrophobic interactions with residues P60b, P60c, and W60d. D167 at the P3 position makes a polar interaction with the backbone N atom of G219 of thrombin, which mimics the interaction of D39 at the P3 position of PAR1. V166 at the P4 position points toward W215 in the aryl binding site. Overall, the binding mode of the P1 to P4 residues of protein C is very similar to that of the P1 to P4 residues of PAR1 and D167 at the P3 position of substrate makes favorable contribution to binding. Values of the B-factor for residues of the protein C peptide are given in parentheses (Å2): Q162 (65), E163 (65), D164 (67), Q165 (68), V166 (46), D167 (37), P168 (34), R169 (32), and L170 (57).