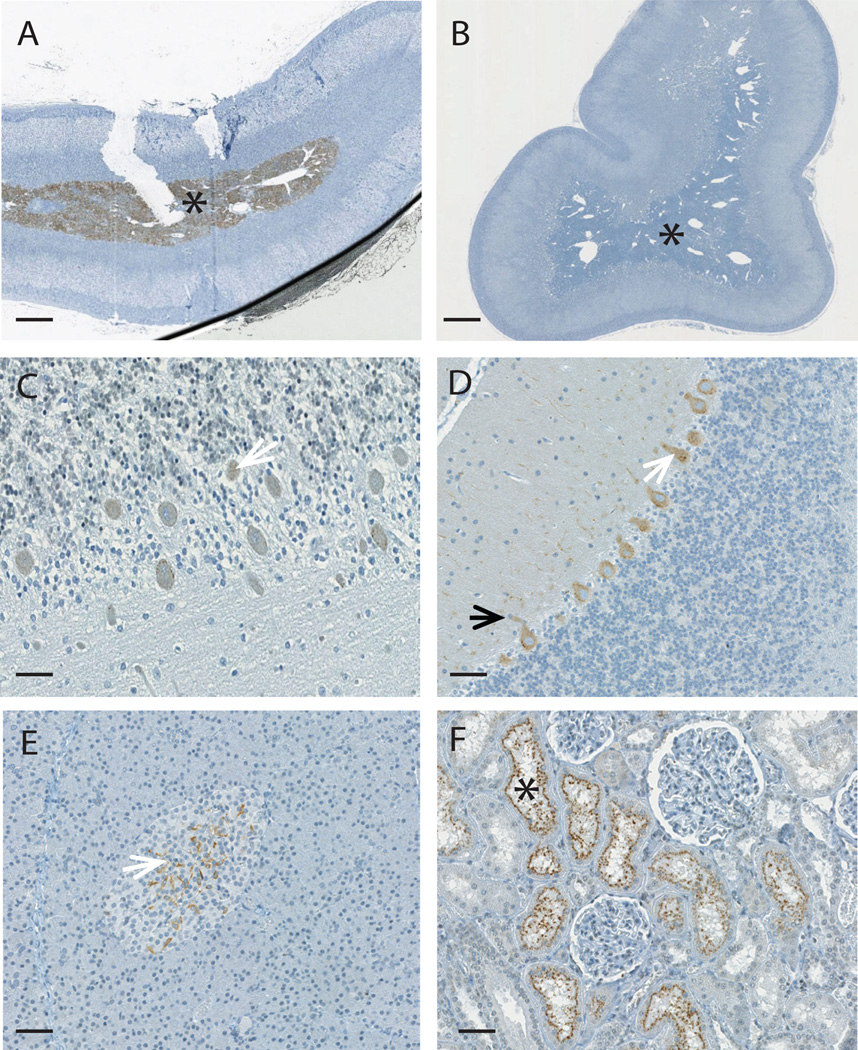
Figure 1. Specific staining with anti-L1O2 RT pAb in the adrenal medulla.
A) At 5 µg/ml the anti-L1O2 RT pAb stained the medullary region (asterisk) of the adrenal gland in mice, human and nonhuman primates (an example from the cynomolgous monkey tissue array is shown). B) The staining could be entirely prevented by peptide competition using 10 µg/ml of the RT peptide. C) At 1µg/ml the anti-HERV-K Gag pAb 4141 stained the cytoplasm of the Purkinje cells (white arrows) in the cerebellum of humans. D) The staining with the anti-HERV-K Gag pAb 4141 was more intense in the nonhuman primates (an example from the rhesus monkey tissue array is shown), and was also seen in the cytoplasm of the axons (black arrow). E) At 1µg/ml the anti-HERV-K Gag pAb 4142 stained occasional cells of the β-islets of the pancreas (white arrow) in human and non-human primates (an example from the cynomolgous monkey tissue array is shown). F) At 1µg/ml the anti-HERV-K Env mAb HERM-1811-5 stained the proximal convoluted tubules (asterisks) of the kidneys of nonhuman primates (an example from the cynomolgous monkey tissue array is shown), but not humans. All images were captured using the NanoZoomer. Magnification is ×20 in parts A and B, with scale bar indicating 500µM and ×200 in parts C–F with scale bar indicating 50µM