Figure 1.
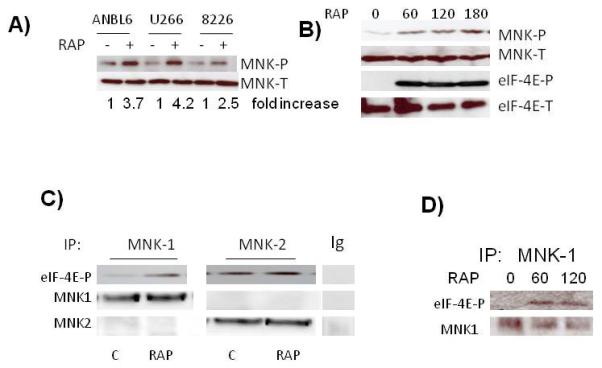
Activation of MNK kinases in MM cells. A) MM cell lines exposed to rapamycin (100 nM) for 3 hrs followed by immunoblot assay for phospho-MNK and total MNK expression. Fold increase is determined by densitometric ratio of MNK-P/MNK-total and represents the mean of 3 independent experiments. Rap-induced increase was significant (p<0.05) in all three cell l ines. B) ANBL-6 cells exposed to rapamycin for 0, 60, 120 or 180 mins, followed by immunoblot assay for phospho-MNK, total MNK, phospho-eIF-4E and total eIF-4E expression. C) MNK1 or MNK2 immunoprecipitated with anti-MNK1, anti-MNK2 antibodies or non-specific IgG, from control or rapamycin (100 nM for 60 mins)-treated ANBL-6 extracts and tested for ability to phosphorylate eIF-4E in vitro. eIF-4E phosphorylation determined by immunoblot. D) MNK1 immunoprecipitated from MM cells after 0, 60 or 120 mins of exposure to rapamycin (100 nM) and tested for phosphorylation of eIF-4E in vitro.
