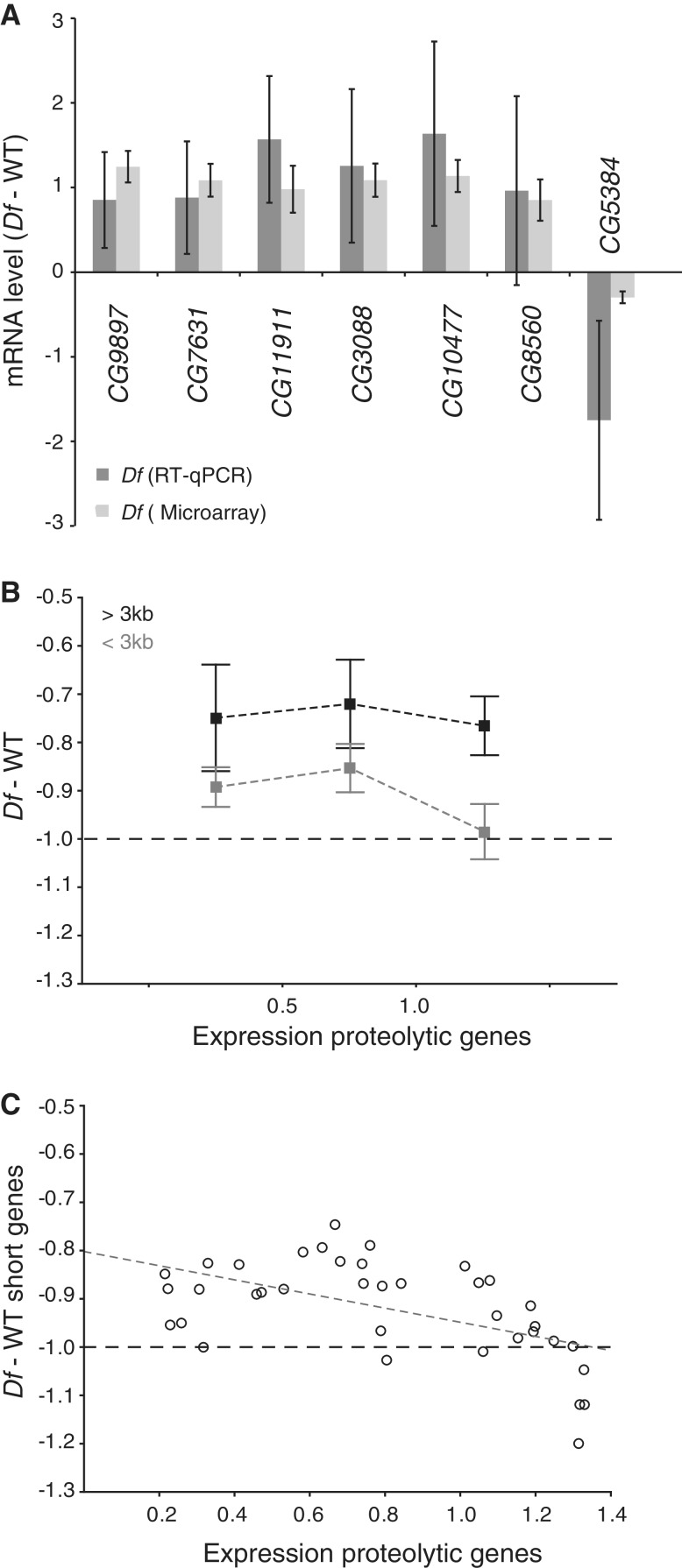
Figure 6.
Aneuploidy induces proteolysis. (A) Comparison of the mean levels of mRNA (log2 scale) from six genes encoding proteolytic proteins and one encoding a deubiquitinating protein (CG5384) determined by RT–qPCR (dark grey bars). The corresponding mean expression ratio for all 38 Df/+ microarray replicates is shown in light grey. Note that a reduction in CG5384 expression is linked to increased proteolysis (31). The mRNA levels measured by qPCR were normalized against that of the Rpl32 gene in each replicate and 100% was set as the mean expression in wild-type. Error bars represent 95% CIs of four biological replicates (qPCR) and 38 biological replicates (microarray). (B) Expression ratios for all long genes (>3 kb, shown in black) within each deficiency region (each replicate represented by a separate data point) and for all short genes (<3 kb, shown in grey) plotted against binned values for the mean expression ratio of the top 20 up-regulated proteolysis genes. Squares indicate mean values and whiskers indicate 95% CIs of n = 10, 12 and 15 for each bin, respectively. (C) Scatter plot of expression ratio for all short genes within each deficiency region plotted against mean expression ratio of the 20 most up-regulated proteolysis genes. The Spearman’s correlation co-efficient is significant (rs = −0.529, p = 7.5 × 10−4). All y-axis values are in log2 scale. Dashed lines represent −1 in log2 scale or 50% of wild-type expression.