Figure 4.
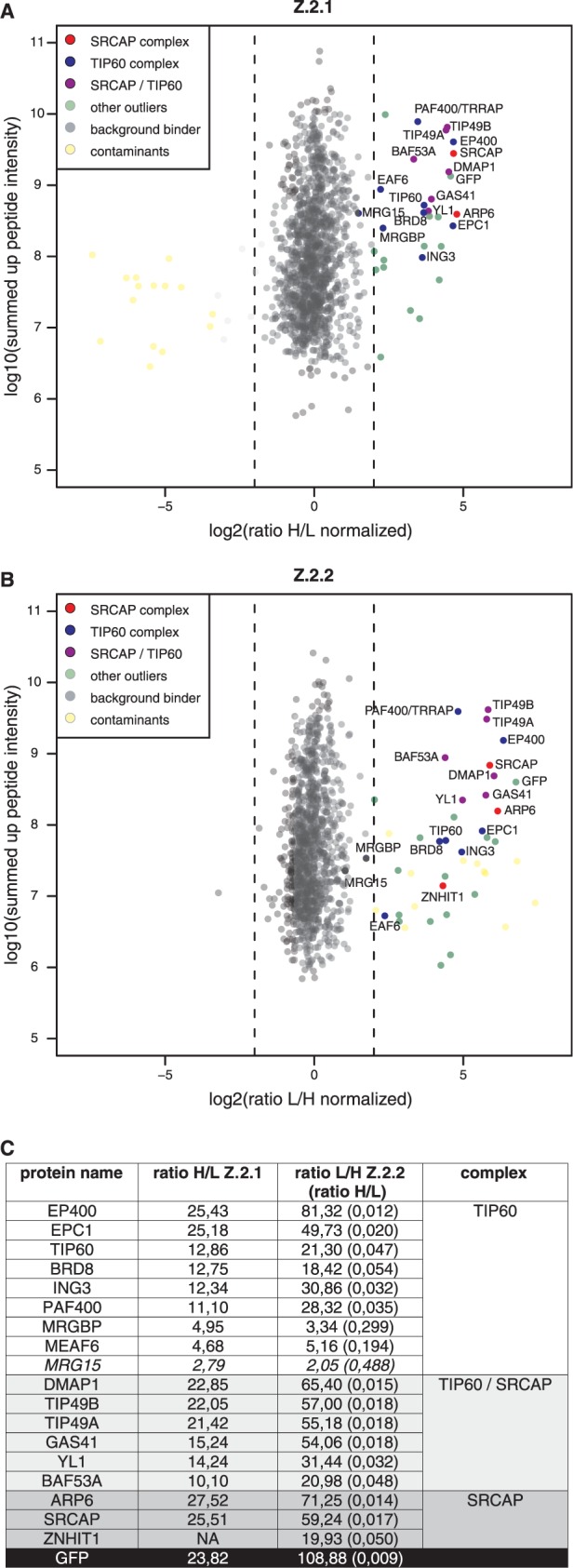
Z.2.2 associates with H2A.Z-specific SRCAP and TIP60 chaperone complexes. GFP-pull-downs for H2A.Z-specific chaperone complexes are shown. HK cells stably expressing GFP-Z.2.1 (A) and GFP-Z.2.2 (B) were SILAC-labeled and subjected to single-step affinity purifications of soluble nuclear proteins in a ‘forward’ (GFP-Z.2.1) or ‘reverse’ (GFP-Z.2.2) pull-down using GFP nanotrap beads. In each panel the ratio of the identified proteins after MS is plotted. Proteins known to interact with H2A.Z are indicated in the following way: members of the SRCAP complex in red, members of the TIP60 complex in blue and shared subunits in purple. Potential novel H2A.Z-interacting proteins are shown as green dots (‘other outliers’) and are distinguished from background binders (gray dots) and contaminants (yellow dots). See also Supplementary Table S1 for a list of all identified proteins. (C) List of the SRCAP and TIP60 complex members and their normalized binding intensity to Z.2.1 or Z.2.2. Note that for comparison reasons the obtained H/L ratios of GFP-Z.2.2 binders (numbers in brackets) were calculated in the corresponding L/H ratios. See also Supplementary Table S1 for a list of all identified proteins and their normalized H/L ratios.
