Table 1.
Optimization of Diethylzinc Addition to 1
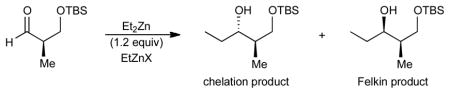
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | temp (°C) | concentration (M)a | LA (mol %)b | drc | yield (%)d |
| 1 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 3.5:1 | <10 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (25) | 5.7:1 | 50 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (50) | 5.7:1 | 61 |
| 4 | 0 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (100) | 7.4:1 | 77 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (150) | 6.5:1 | 83 |
| 6 | −15 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (150) | 6.9:1 | 83 |
| 7 | −30 | 0.2 | EtZnCl (150) | 5.2:1 | 61 |
| 8 | 0 | 0.5 | EtZnCl (150) | 8.9:1 | 89 |
| 9 | 0 | 0.5 | EtZnBr (150) | 7.9:1 | 85 |
| 10 | 0 | 0.5 | EtZnOTf (150) | 15.5:1 | 78 |
| 11 | 0 | 0.5 | EtZnONf (150) | 10:1 | 87 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.5 | EtZnN(Tf)2 (150) | 6:1 | 72 |
Concentration is with respect to the aldehyde.
mol % of Lewis acid is with respect to the aldehyde.
dr determined by 1H NMR of the unpurified product or by GC analysis of the TMS-protected product derivatives and refers to the ratio of chelation:Felkin addition products.
Refers to yield of isolated, purified product.
