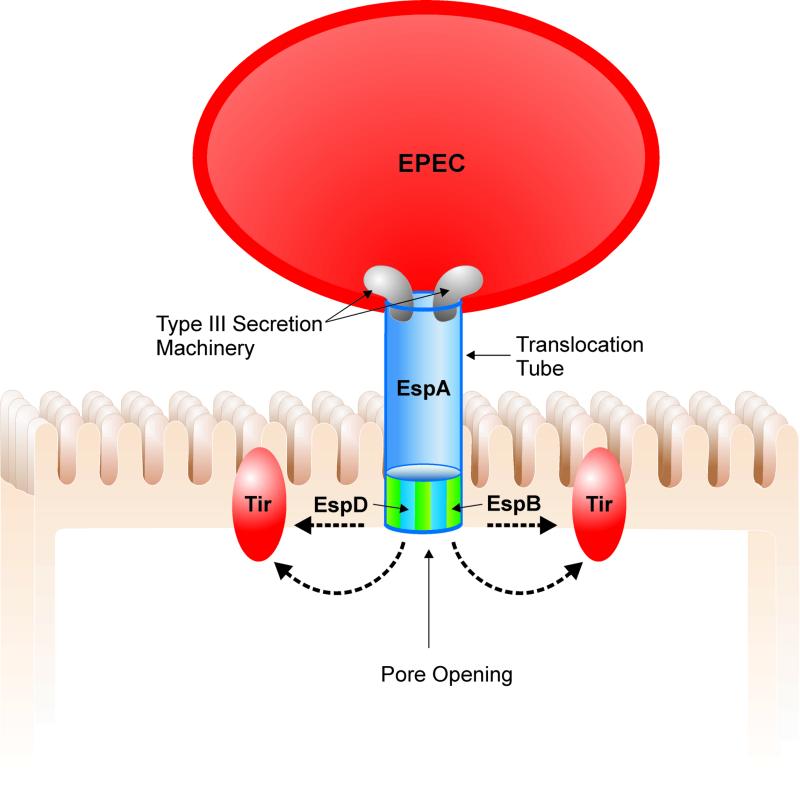
Figure 1.
Translocation of EPEC-secreted proteins (Esps) occurs through a type III secretion system that forms a pore through EPEC's membranes. Once translocated outside the bacteria, EspA forms a filamentous translocation tube whereas EspB and EspD are inserted into the host cell membrane, putatively forming a pore structure, allowing the passage of other effector proteins, such as Tir into the host cell membrane.