Fig. 5.
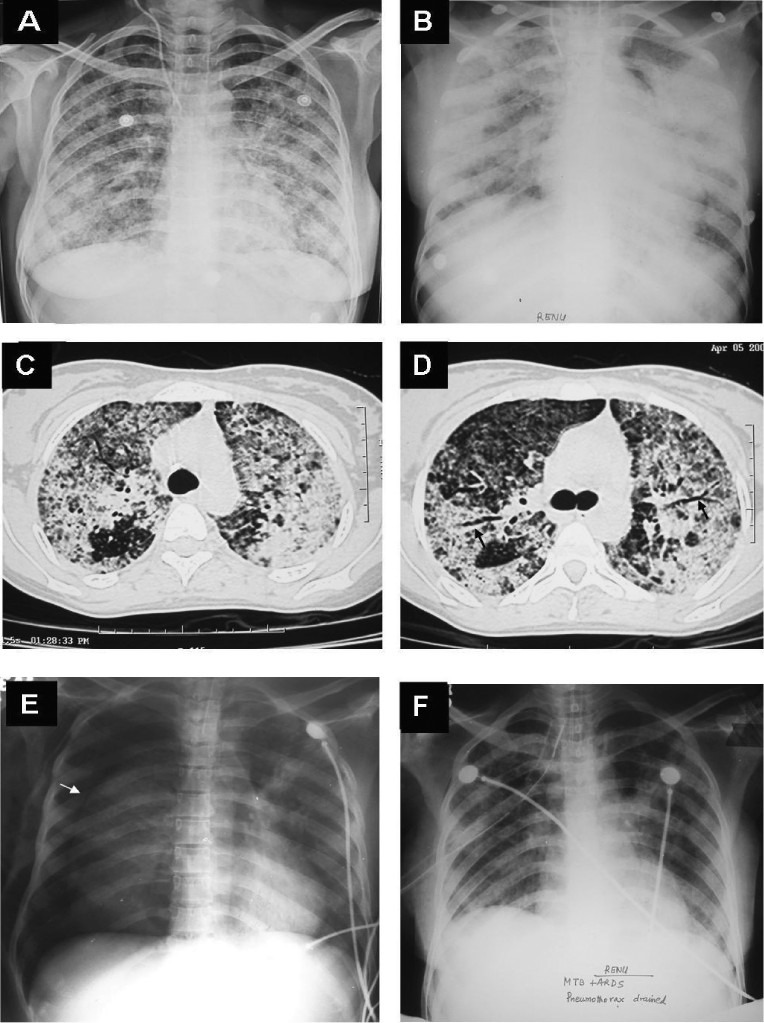
Chest radiograph (postero-anterior view) of a pregnant woman who presented with prolonged pyrexia showing a classical miliary pattern (A). Fundus examination following mydriatic administration in both the eyes revealed choroid tubercles and had raised the suspicion of miliary TB. The patient developed ARDS during the course of her illness. Chest radiograph (antero-posterior view), obtained with a portable X-ray machine, bed-side showing bilateral frontal opacities suggestive of ARDS (B). CT chest obtained at the same time reveals air-space consolidation (C and D); air-bronchogram (arrow) (D). While assisted ventilation was being administered, the patient developed pneumothorax (asterisk) on the right side; collapsed lung border is also evident (arrow) (E). The patient required tube thoracostomy and underwater seal drainage. Eventually the patient was weaned off the ventilator and the intercostal tube was removed following resolution of the pneumothorax. The chest radiograph obtained thereafter shows significant improvement in the lesions (F). The patient survived the turbulent in-hospital course, went on to complete full-term of pregnancy and was successfully delivered a live baby. ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CT, computed tomography; TB, tuberculosis.
