Fig. 8.
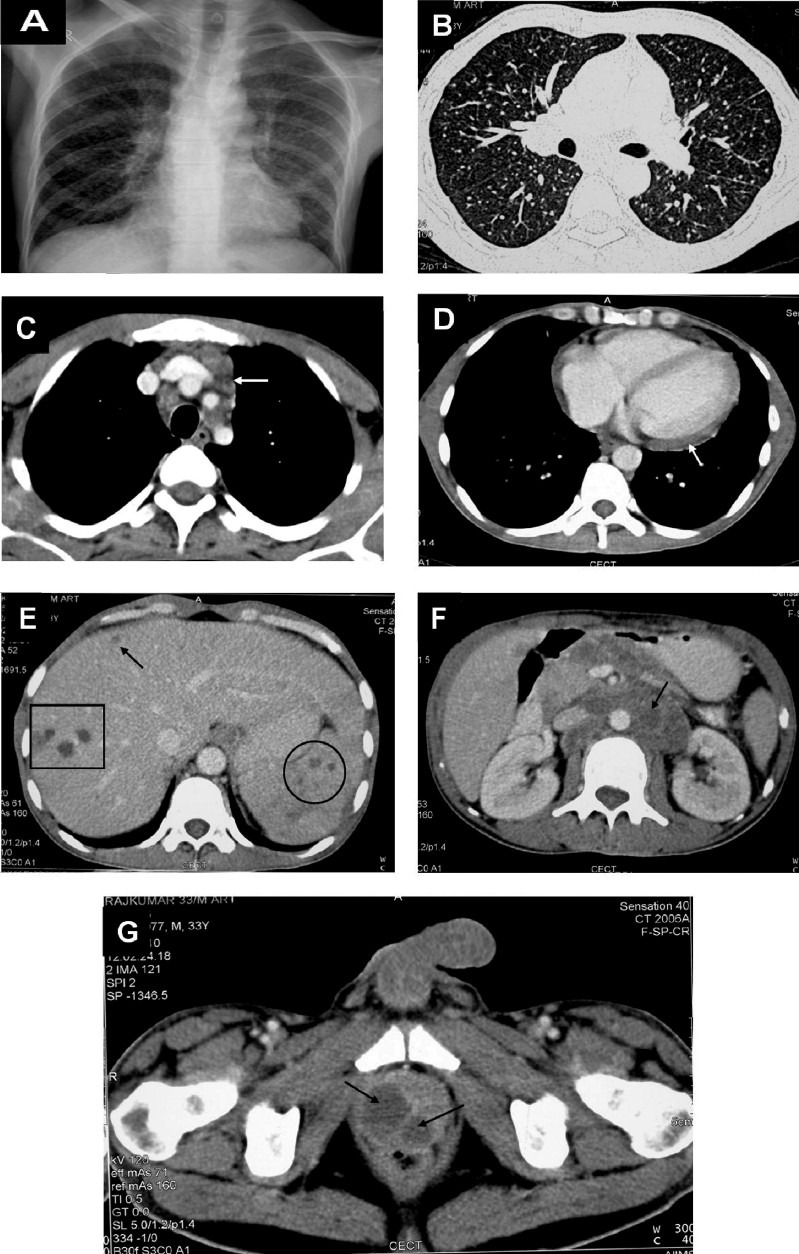
Chest radiograph in a patient with HIV/AIDS (postero-anterior view) (A) and chest CT (lung window) (B) showing classical miliary pattern. The CECT chest (mediastinal window) also reveals intrathoracic lymphadenopathy (arrow) (C) and pericardial thickening and effusion (D). The CECT of the abdomen of the same patient reveals focal miliary lesions in the liver (square, arrow) and spleen (circle) (E) and retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy (arrow) (F); pelvic CECT shows a prostatic abscess (arrows) (G). Ultrasound guided trans-rectal prostatic aspirate smear and culture examination confirmed the diagnosis of miliary TB. The diagnostic evaluation of this patient illustrates the judicious use of imaging modalities to define the extent of organ system involvement and procuring tissue for diagnostic confirmation. Such extensive involvement usually occurs in HIV/AIDS with miliary TB. HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; CT, computed tomography; CECT, contrast enhanced computed tomography; TB, tuberculosis.
