Figure 2.
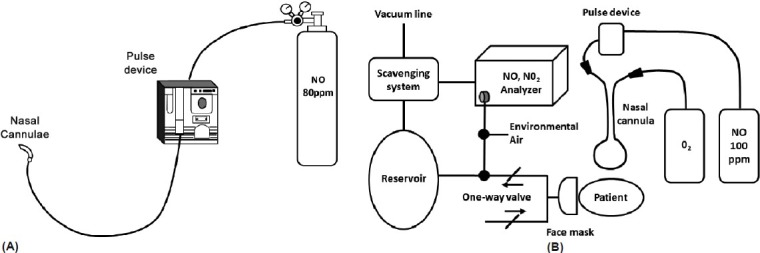
Examples of pulsed inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems used in clinical studies: (A) Ambulatory system. Reproduced with permission from the American College of Chest Physicians, Chest, Volume 109, Richard N. Channick, John W. Newhart, F. Wayne Johnson, Penny J. Williams, William R. Auger, Peter F. Fedullo, and Kenneth M. Moser, pulsed delivery of inhaled nitric oxide to patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: an ambulatory delivery system and initial clinical tests, pp 1545–1549, Copyright (1996), American College of Chest Physicians;[48] (B) Hospital system. Reprinted with permission from Internal Medicine, Volume 41, Osamu Kitamukai, Masahito Sakuma, Tohru Takahashi, Jun Nawata, Jun Ikeda, and Kunio Shirato, hemodynamic effects of inhaled nitric oxide using pulse delivery and continuous delivery systems in pulmonary hypertension, pp 429–434, Copyright The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine (2002).[49] iNO: inhaled nitric oxide NO2: nitrogen dioxide
