Figure 5.
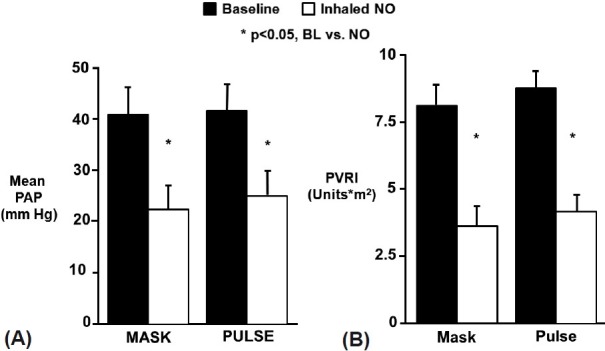
Delivery of inhaled NO by continuous mask or pulsed nasal cannula was equally effective in lowering mean pulmonary artery pressure (A) and pulmonary vascular resistance index (B). PAP: mean pulmonary artery pressure; PVRI: pulmonary vascular resistance index; iNO: inhaled nitric oxide; BL: baseline. Reprinted from The Journal of Pediatrics, Vol 133, D. Dunbar Ivy, Jeffrey L. Griebel, John P. Kinsella, and Steven H. Abman, acute hemodynamic effects of pulsed delivery of low flow nasal nitric oxide in children with pulmonary hypertension, Pages No. 453–456, Copyright (1998), with permission from Mosby, Inc.[50]
