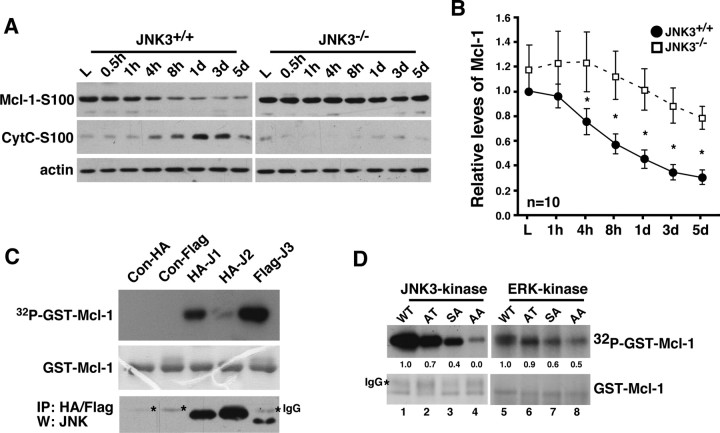
Figure 3.
JNK3 regulates Mcl-1 stability after injury. A, Mcl-1 protein levels change most dramatically beginning 4 h after injury in JNK3+/+ mice, coinciding with cytC release. In JNK3−/− mice, the Mcl-1 levels remain elevated. Actin control is shown; the control for fractionation is shown in Figure 2C. B, Quantification of the relative Mcl-1 levels at different time points after injury. Asterisks represent the time points at which the two genotypes show statistical difference (Student's t test, p < 0.05). C, JNK3 phosphorylates Mcl-1 in vitro. JNK1, 2, or 3 was immunoprecipitated from 293T cells and subjected to kinase assays, using GST-Mcl-1 as the substrate. The asterisks in the stained gel represent IgG. As a control, the same lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation and blotted for JNK Western. The experiments were repeated three to four times with similar results. D, JNK3 phosphorylates Mcl-1 at both S121P and T163P, whereas ERK phosphorylates Mcl-1 at T163P in vitro. GST-Mcl-1 proteins bearing single and double mutations as indicated were used as substrates in kinase reactions. The bottom panels show the amount of GST-Mcl-1 protein in each lane as Coomassie-stained controls. The asterisk in the stained gel represents IgG. The experiments were repeated three to four times with similar results.