Figure 1.
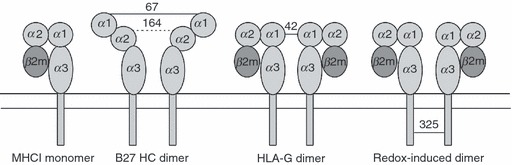
Depiction of MHC monomer and various dimeric forms of MHCI molecules. From left to right; typical monomer MHCI molecule; partially unfolded HLA-B27 dimers, formed at the cell surface by disulphide linkage through residue cysteine 67 in the peptide-binding groove, but also contributed to in the endoplasmic reticulum by cysteine at position 164; HLA-G dimer formed through disulphide linkage at cysteine at position 42; redox-induced dimers formed on cells undergoing apoptosis and on exosome vesicles as the result of altered intravesicle or cytoplasmic redox conditions, formed through cysteines in the cytoplasmic tail domains (typically positions 325 in HLA-B alleles, and 339 in HLA-A alleles).
