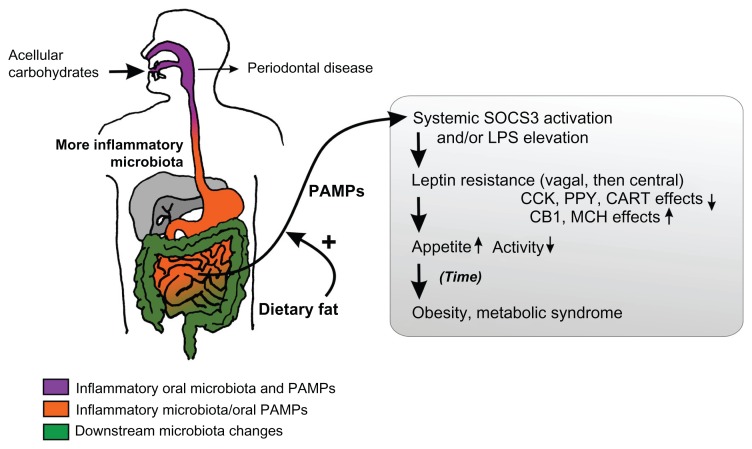
Figure 2.
Schematic of the hypothesis.
Notes: The acellular dense carbohydrates of modern foods are proposed to produce an inflammatory microbiota from the mouth onwards, initially producing periodontal disease. The small bowel is exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and other pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from the oral microbiota, and proinflammatory modulation of its own small populations of bacteria by concentrated acellular carbohydrates. With systemic absorption enhanced by dietary fat, the inflammatory bacterial compounds induce leptin resistance and hyperphagia. The contents of the gray box represent the existing understanding of the effects of diet-induced obesity on energy homeostasis.
Abbreviations: CCK, cholecystokinin; PPY, peptide YY; CART, cocaine and amphetamine related transcript; CB1, cannabinoid receptor type 1; MCH, melanin concentrating hormone.